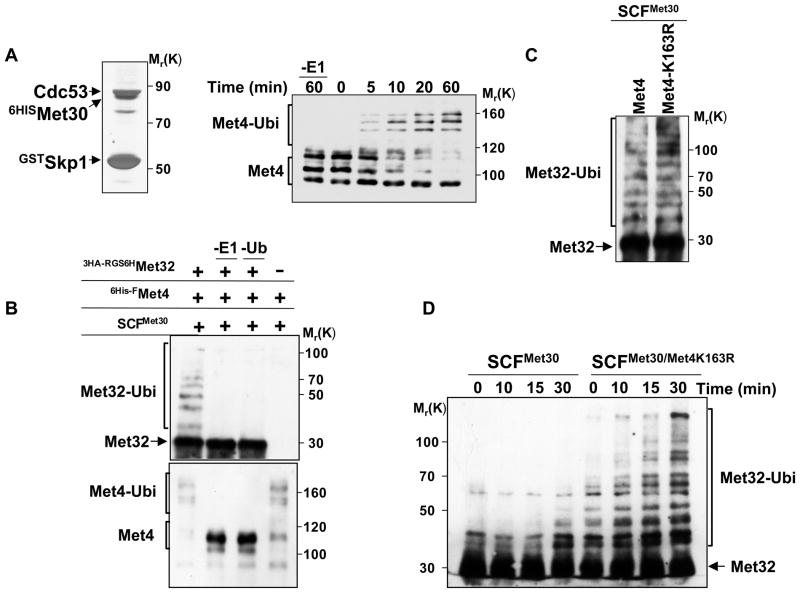
Figure 6. In vitro reconstitution of Met32 ubiquitylation by the SCFMet30/Met4 ubiquitin ligase.
(A) Recombinant, active SCFMet30. Recombinant SCFMet30 was purified on glutathione beads from insect cells co-expression GstSkp1, Cdc53, 6HisMet30, and Rbx1. Complexes were eluted, separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining (left panel). The activity of the recombinant SCFMet30 was assayed by in vitro ubiquitylation of Met4 as described (Aghajan et al., 2010; Chandrasekaran et al., 2006). Reaction products were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Met4 antibodies. The asterisk indicates a cross-reacting band.
(B) In vitro ubiquitylation of Met32 by recombinant SCFMet30/Met4. Immobilized SCFMet30/Met4 complex were incubated with RGS6H-3HAMet32 purified from E. coli. The ligase-substrate complex was eluted with glutathione, and then incubated for 3 hrs at 30°C with ubiquitylation reaction mixture. Reactions were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA and anti-Met4 antibodies.
(C) Met4K163R recruits Met32 to SCFMet30 and mediates Met32 ubiquitylation. Experiments as in panel B except that SCFMet30/Met4 and SCFMet30/Met4K163R were used as ubiquitin ligases.
(D) Met4 stimulates ubiquitylation of Met32.
Recombinant SCFMet30/Met4K163R complexes were purified as described above, eluted with glutathione and combined with purified RGS6H-3HAMet32 (25nM final concentration). Ubiquitylation reaction mixture was added and the reaction incubated at 30°C for the indicated time intervals. Reaction products were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA antibodies.