Fig. 1.
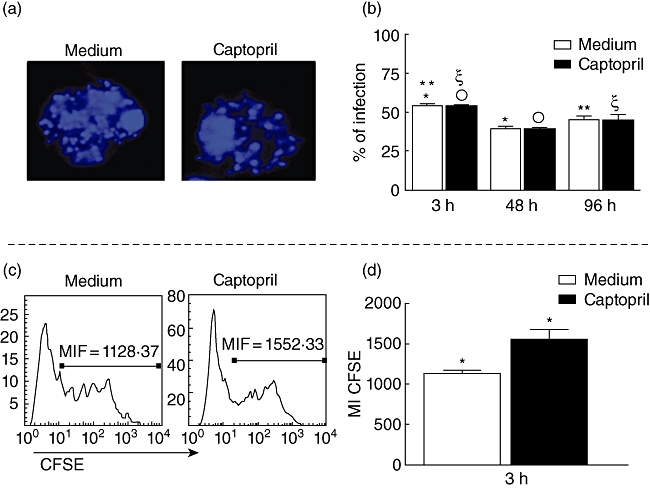
Determination of infectivity in monocytes by Y strain trypomastigotes, treated or not with captopril. (a) Representative confocal microscope analysis image, showing 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI+) parasite's nuclei inside monocytes. Cells were treated or not with captopril, infected with five parasites/cell, preparations were stained with DAPI, and read on a confocal microscope, as described in Material and methods; magnification ×62; (b) determination of the percentage of infected cells after 3, 48 and 96 h of infection in cultures treated or not with captopril, using confocal microscopy analysis; cells were prepared as described above, acquired by confocal microscopy, and the percentage of infected cells was determined by counting the total number of cells and the parasite+ cells; results are expressed as average ± standard deviation. (c) Representative histogram of peripheral blood mononuclear cells exposed to Y strain trypomastigotes labelled with 5- and 6-carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE), to determine the intensity of CFSE in cultures treated or not with captopril, as described in Material and methods. Briefly, cells were infected with five CFSE-labelled parasites/cell and incubated for 3 h; after this period, samples were read by fluorescence activated cell sorter and the fluorescence mean intensity was analysed. (d) Determination of the mean intensity of expression of CFSE fluorescence as a measure of intensity of infection in cells from cultures treated or not with CFSE; results are expressed as average ± standard deviation. Identical symbols indicate P < 0·05 between groups marked with the same symbol.
