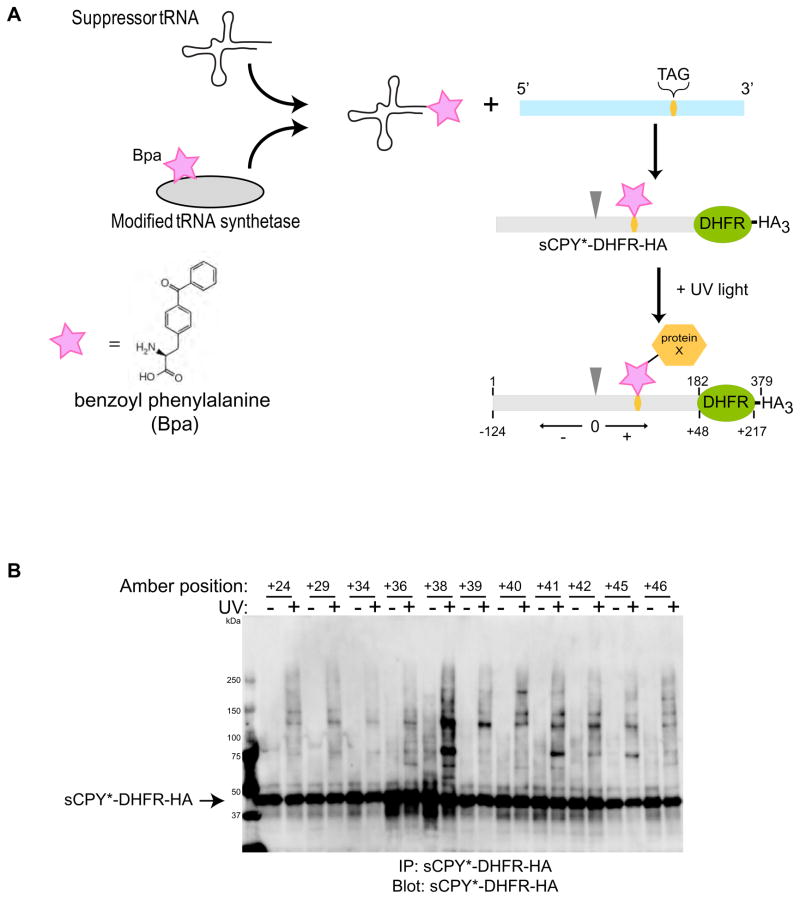
Figure 3. Site-specific in vivo crosslinking of an ERAD-L substrate.
(A) A shortened version of CPY* containing the last 180 amino acids, including the glycosylation site, was fused to dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and three HA tags (sCPY*-DHFR-HA). Single amber stop codons (TAG) were introduced at different sites of the coding sequence. The stop codon was suppressed in vivo by expression of a suppressor tRNA that is charged with the photoreactive amino acid analog benzoyl phenylalanine (BPA) by a modified amino acyl tRNA synthetase. UV irradiation leads to crosslinks with proteins in close proximity of the photoreactive probe. The position of the probe is defined relative to the glycosylation site (position 0; arrow head; corresponds to position 124 in sCPY*-DHFR-HA), with amino acid residues upstream and downstream given negative and positive numbers, respectively.
(B) Photoreactive probes were placed at the indicated positions and the cells were irradiated with UV light, as indicated. Detergent-solubilized membranes were subjected to immunoprecipitation with HA antibodies, and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with HA antibodies.
See also Figure S4.