Figure 4. Neuroprotective effects of systemic MB against sodium azide-induced neurotoxicity in the PCC.
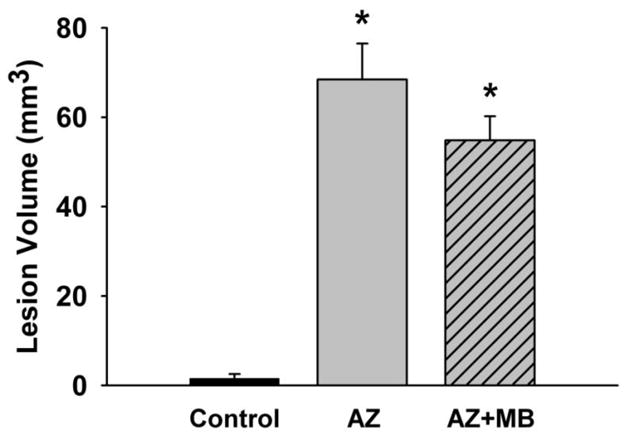
Quantitative group data for the unbiased stereological analysis of the metabolic lesion volume produced by AZ injections into the PCC. The sham operated control group had less than 2 mm3 of PCC volume affected. The AZ group showed a PCC lesion volume of about 70 mm3, whereas the AZ+MB group had a reduced lesion volume averaging 55 mm3. Therefore, MB treatment induced a total 20% bilateral decrease in the volume of PCC and contiguous cortex affected by structural damage due to cytochrome oxidase inhibition induced by the local infusion of sodium azide. * = significantly different from control, p < 0.001.
