Fig. 1.
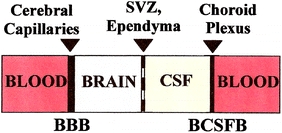
Anatomical relationships among the BCSFB, CSF, and BBB: neurons receive supplies from two sources: the nearby cerebral capillaries or BBB (mainly glucose, amino acids and free fatty acids) and the more distant CP or BCSFB (mainly vitamins, growth factors, neurotrophins, and hormones). Both the BBB and BCSFB reabsorb neural waste products and unneeded proteins into blood. The brain microvessel endothelium and CP epithelium both have tight junctions that restrict diffusion of small water-soluble molecules: therefore ion and organic solutes are actively transported via membrane carriers (structural proteins) across the barriers. Ependyma is a single-cell epithelial layer with highly permeable gap junctions that allows free exchange of solutes paracellularly between brain ISF and ventricular CSF
