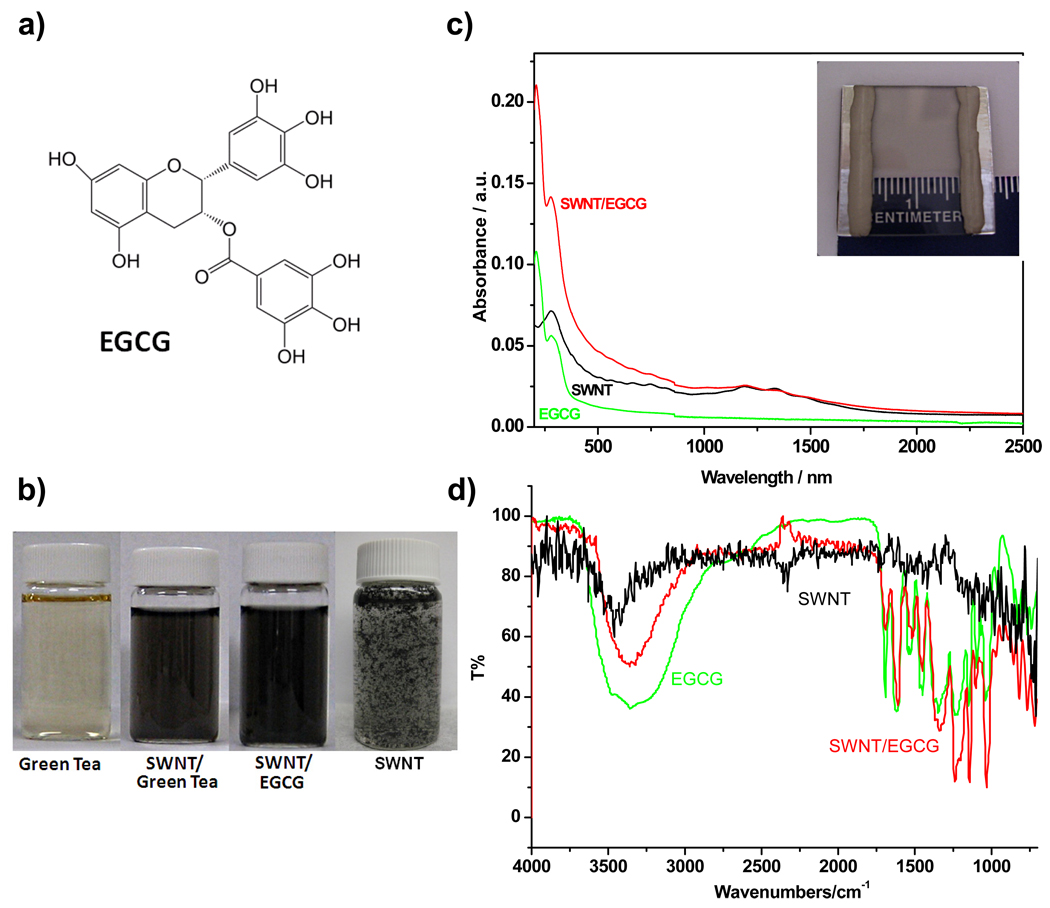
Figure 1.
(a) Chemical structure of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). (b) Photograph of four vials with green tea (left), SWNT and green tea (middle left), 4.4 × 10−4 M EGCG sonicated with ca. 1 mg of SWNTs (middle right) and SWNTs in water (right). (c) UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra of SWNT (black), EGCG (green), and SWNT/EGCG (red) as thin films on quartz. Inset displays a photograph of transparent SWNT/EGCG conductive film on a quartz slide. (d) FTIR spectrum of bare SWNTs (black), EGCG in MeOH (4×10−4 M) (green) and SWNT/EGCG composite after heating at 140 °C for 20 min (red).