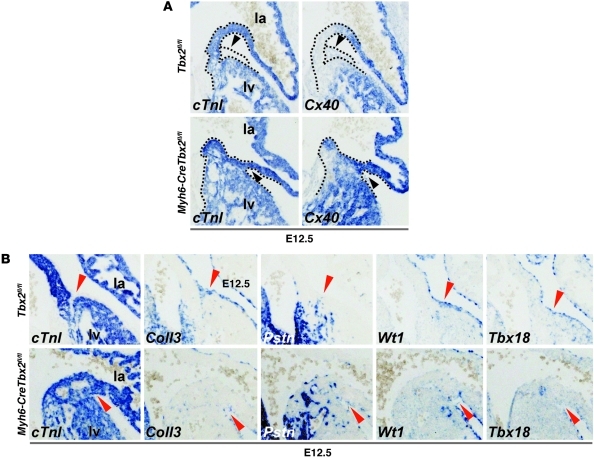
Figure 5. Absence of Tbx2 in the AV canal myocardium leads to absence of epicardial derived mesenchyme and abnormal epicardial patterning.
(A) In situ hybridization analyses of E12.5 Tbx2fl/fl and Myh6-CreTbx2fl/fl embryos. When Tbx2 is inactivated within the myocardium Cx40 is ectopically expressed in the shortened and broadened AV canal myocardium. Furthermore, the accumulation of epicardial derived mesenchyme in the left AV sulcus is lost (black arrowheads). Dashed lines depict the contours of the myocardium (cTnI+) and epicardial sulcus (cTnI–) in the AV region. (B) Tbx2 in the AV canal myocardium is required for correct patterning of the epicardium and the accumulation of epicardial derived mesenchyme in the AV sulcus. In situ hybridization analyses of E12.5 Tbx2fl/fl and Myh6-CreTbx2fl/fl embryos is shown. In Tbx2fl/fl embryos, the epicardium derived mesenchyme accumulates specifically in the AV sulcus and invaginates in between the atria and ventricles. Col3a1 (Coll3), Tbx18, and Wt1 are expressed in the epicardium and epicardial derived mesenchyme that also expressed Postn (Pstn). In the Myh6-CreTbx2fl/fl embryos, the epicardial derived mesenchyme fails to accumulate in the AV sulcus, and the examined genes are aberrantly expressed (red arrowheads). Original magnification, ×10 (A and B).