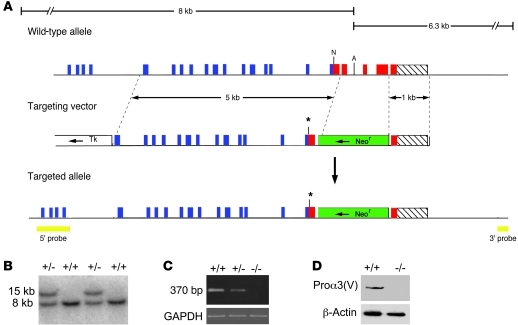
Figure 1. Targeted disruption of Col5a3.
(A) Structure of the targeting vector and Col5a3 locus, before and after homologous recombination. Horizontal arrows mark directions of transcription of neor and tk cassettes. Blue, red, and hatched boxes represent COL1, C-propeptide, and 3′-UTR exons, respectively. The green boxes represent the Neor cassette; the yellow boxes represent 5′ and 3′ external probes. The asterisks mark the site of a premature stop codon engineered via blunt-end ligation of a NarI site. A, AflII; N, NarI. (B) Southern blot of AflII-restricted genomic DNA from wild-type and correctly targeted ES cell clones hybridized to the 5′ probe. (C) RT-PCR analysis of total RNA from 15.5-dpc embryos detected a 370-bp amplimer corresponding to wild-type Col5a3 RNA in wild-type (+/+) samples that was diminished in Col5a3+/– (+/–) samples and absent in Col5a3–/– (–/–) samples. Amplification of a GAPDH product was a loading control. (D) Immunoblotting of 15.5-dpc embryo homogenates detects pro-α3(V) chains in wild-type but not Col5a3–/– samples. Reprobing with anti–β-actin antibody controlled for protein loading.