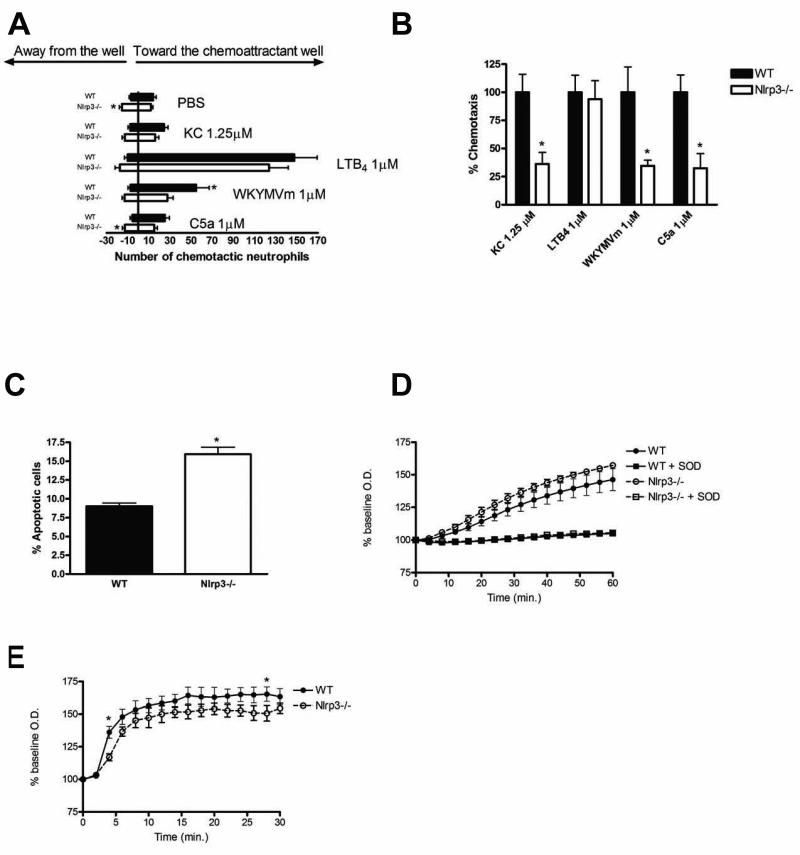
Figure 5.
Chemotaxis and spontaneous apoptosis are altered in BM-derived neutrophils isolated from Nlrp3−/− mice. (A) Overall neutrophil movement in response to PBS (vehicle control), KC (1.25 μM), leukotriene B4 (1 μM), WKTMVm (1 μM) and C5a (1 μM) as assessed with an under-agarose assay. (B) Neutrophil chemotaxis expressed as the number of cells that migrated towards the chemoattractant as a percentage of the total number of cells that moved in any direction. N=4; * denotes p<0.05 compared to WT cells. (C) Spontaneous apoptosis of BM-derived neutrophils after 12h in culture as assessed by flow cytometry. N=4; * denotes p<0.05 compared to WT cells. (D-E) Assessment of PMA(8 μM; D)- and fMLP(8 mM; E)-induced superoxide production in BM-derived neutrophils isolated from WT and Nlrp3−/− mice. N=4, * denotes p<0.05 compared to WT cells. Addition of superoxide dismutase (SOD, 1500 U) was employed as a control to quench superoxide accumulation (D).