Figure 1. Expression of ADI-1, ADI-2 and ADI-3 genes in T. vaginalis.
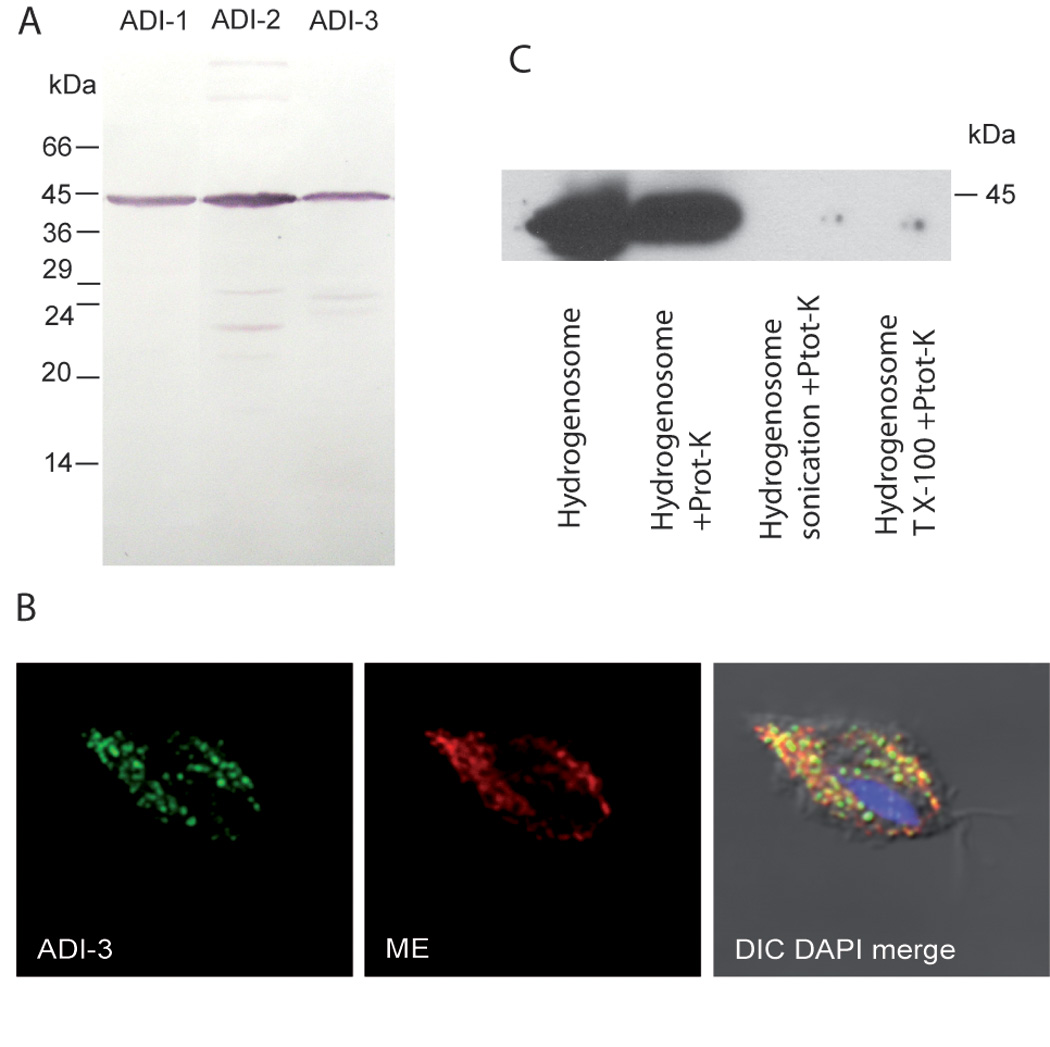
A) Each gene was expressed with C-terminal hemaglutinin tag in T. vaginalis and detected in cellular lysates by immunoblotting with anti-hemaglutinin monoclonal antibody. B) Representative localization of ADI in T. vaginalis hydrogenosomes by confocal fluorescent microscopy. ADI-3, fluorescent microscopy of T. vaginalis expressing ADI-3. Mouse monoclonal anti hemaglutinin (ADI-HA) tag antibody was used to visualize ADI-3 (green); ME, fluorescent microscopy of rabbit polyclonal anti malic enzyme antibody (red); DIC DAPI merge, merged image of ADI-3-HA, ME image stained with DAPI (blue) to show the nucleus. C) ADI localizes to the inside of hydrogenosomes. Treatment of intact hydrogenosomes with proteinase K (Prot-K) did not affect signal for ADI-1, while ADI-1 was not detected by immunobloting when hydrogenosome membranes were disintegrated by sonication or Trition X-100 (T X-100) and subsequently treated with proteinase K.
