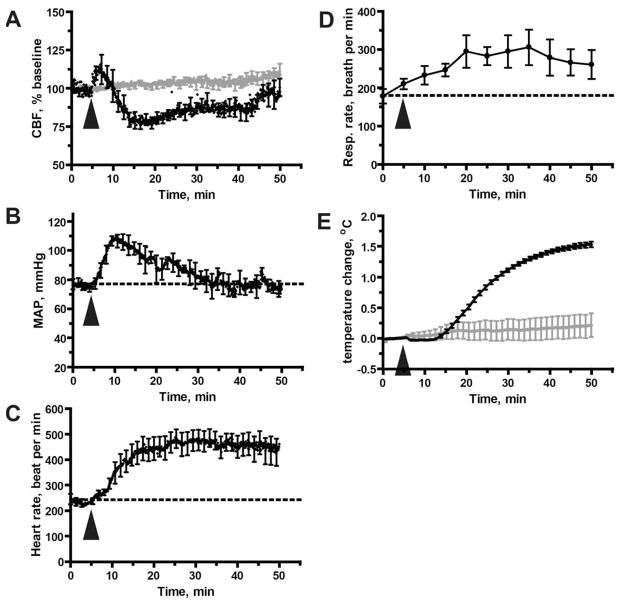
Figure 1. Acute MA exposure (5 mg/kg) disregulates CBF and modulates other physiological parameters.
A. Disregulation of CBF as measured by laser Doppler flowmetry. Values are expressed as a percentage of baseline CBF, defined here as the mean CBF measured during the 5 minute period immediately preceding delivery of MA (or saline, shown in grey). Results represent mean from 5 mice treated with MA and 3 mice treated with saline. B. MA-induced hypertension. Mean arterial blood pressure was measured via a catheter inserted into the femoral artery; results shown represent mean data values from 6 mice per group. C. Increase in heart rate. Results represent data from the same mice shown in (B). D. Increase in respiratory rate; results shown are mean data values from 8 mice. E. MA-induced hyperthermia. Body temperature was measured with a rectal probe, and results are presented relative to baseline temperature (calculated as in (A)). Injection of saline did not induce hyperthermia (shown in grey). Results represent data from the same mice shown in (A). (A–E) All data represent mean ± SEM. The arrowhead indicates the time at which MA (or saline) was injected.