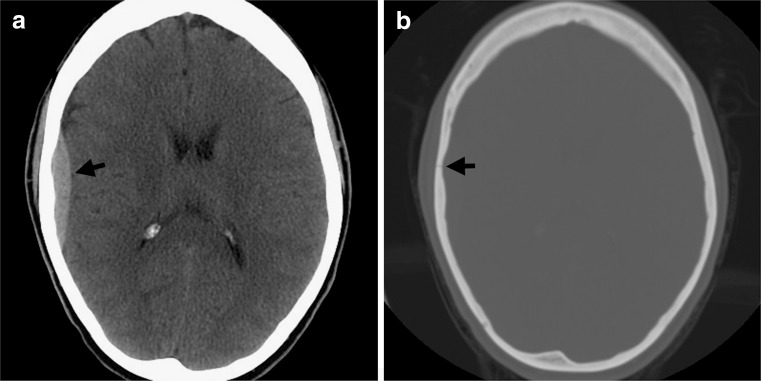
FIG. 1.
Classic arterial epidural hematoma. (a) Axial noncontrast CT in brain windows shows a lentiform, high attenuation collection (arrow) adjacent to the right temporal lobe, consistent with an EDH caused by injury to a branch of the middle meningeal artery. (b) The skull fracture that is almost invariably seen with an EDH is best appreciated on bone windows (arrow). CT = computed tomography; EDH = epidural hematoma. (High resolution version of this image is available in the electronic supplementary material.)