Figure 7. The stimulatory efficacy of polylysine on CK2 holoenzyme is reduced by the CFTRΔF peptide.
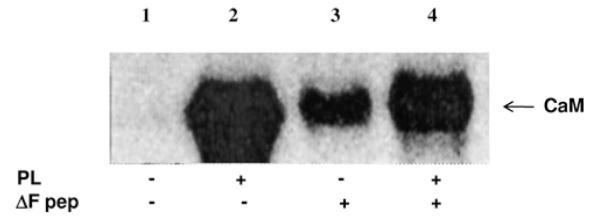
Calmodulin (CaM) underwent phosphorylation by CK2 holoenzyme in the absence (lane 1) or presence of either 330 nM polylysine (PL), 80 μM CFTRΔF peptide (lanes 2 and 3 respectively) or both (lane 4). The stimulatory effect of polylysine observed in lane 2 was attenuated by the CFTRΔF peptide (lane 4), which by itself is capable of enhancing phosphorylation of CaM (lane 3), albeit much less efficiently than polylysine. These results argue for a competition between polylysine and the CFTRΔF peptide for the same anchoring site.
