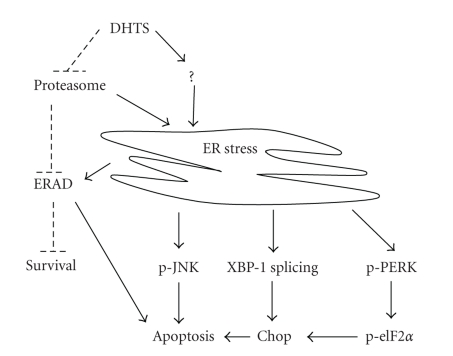
Figure 7.
The possible mechanisms of DHTS-induced ER stress and apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma cells. First, DHTS may induce ER stress through inhibiting proteasome activity or unknown pathways. Second, ER stress induces UPR as evidenced by the upregulation of GRP78/Bip, CHOP/GADD153, and XBP1 mRNA splicing forms as well as increase of the phosphorylation of eIF2α and JNK. In addition, ER stress may induce ERAD, which degrades misfolded proteins mediated by proteosome. Third, prolonged ER stress causes cells to undergo apoptosis through activation of CHOP and JNK, and further promoting apoptosis through inhibition of ERAD by DHTS. Solid lines are used to indicate activating pathways, and dashed lines are used to indicate inhibiting pathways.