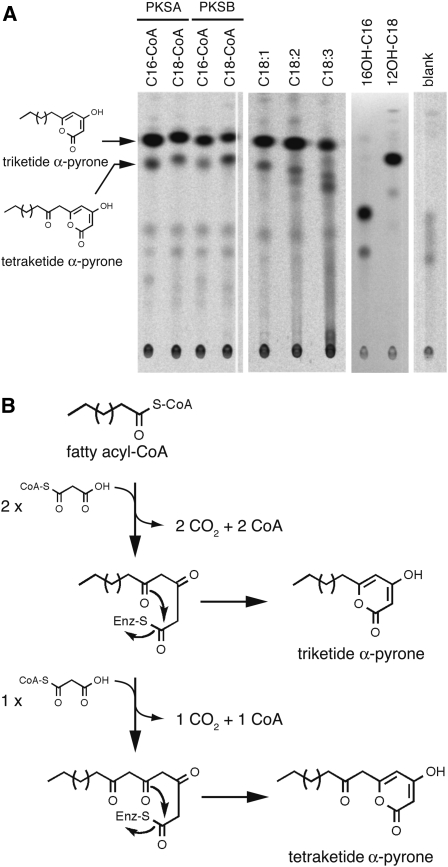
Figure 10.
TLC Analysis of Radiolabeled Reaction Products of PKSs.
Recombinant proteins produced by bacteria were incubated with different CoA esters as starters and 14C-malonyl-CoA as extender. Radioactive reaction products were separated by TLC and detected using a phosphor imager.
(A) Left panel: Chemically synthesized CoA esters used as starters are indicated above each lane. PKSA or PKSB was incubated as indicated. The structures of the major reaction products as deduced from LC-MS/MS analysis are shown on the left. Middle panel: The CoA esters synthesized after incubation of ACOS5 with unsaturated fatty acids as substrates were incubated with PKSB and malonyl-CoA. Tri- and tetraketide reaction products were identified by LC-MS/MS. Right panel: After incubation of 16-OH palmitic or 12-OH stearic acids in the presence of ACOS5, the resulting esters were condensed with malonyl-CoA by PKSB, yielding corresponding tri- and tetraketide α-pyrones. Blank was run without addition of fatty acyl-CoA. No products were observed without addition of PKSA or PKSAB.
(B) Putative mechanism of fatty acyl-CoA condensation with malonyl-CoA catalyzed by PKSs. After two rounds of extension with malonyl-CoA, the intermediate compounds may form a cyclic lactone, yielding triketide α-pyrones, or undergo an additional round of extension yielding the tetraketide α-pyrone compounds.