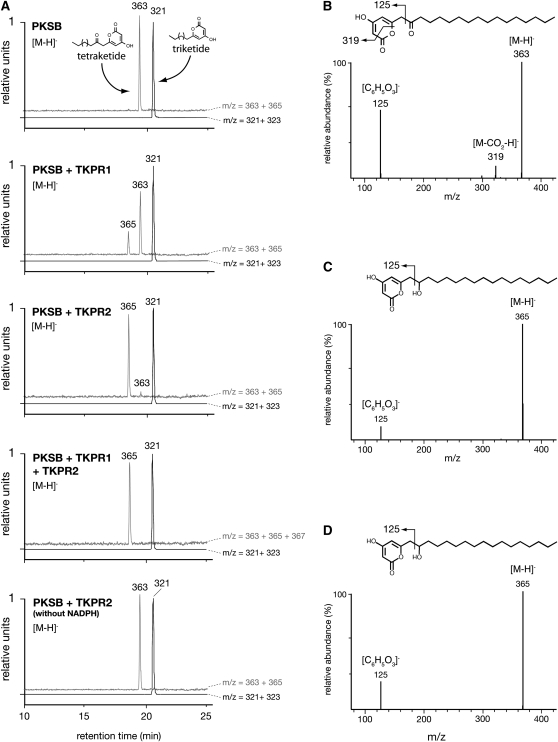
Figure 7.
Identification of TKPR Reaction Products by LC-MS/MS.
Tri- and tetraketide compounds were synthesized by PKSB in the presence of palmitoyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA and incubated with recombinant TKPR enzymes. Reaction products were separated by UPLC and identified by negative electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry.
(A) Compounds were detected by their m/z values. Black curves show ions corresponding to the triketide compound and its putative reduction product (m/z of 321 and 323, respectively); gray curves show ions corresponding to the tetraketide compound and its putative reduction product (m/z of 363 and 365, respectively). The 321 (triketide) and 363 (tetraketide) peaks of the control incubated without NADPH (bottom profile) have been normalized to 1. Only the tetraketide compound was substrate for TKPR1 and TKPR2. No product corresponding to a double reduction of the tetraketide substrate (m/z = 367) was detected when TKPR1 and TKPR2 were incubated together.
(B) Fragmentation pattern of [M-H]− ion of the tetraketide substrate (m/z = 363) and putative fragmentation scheme of the molecule.
(C) Fragmentation pattern of [M-H]− ion of the reduced product obtained after incubation with TKPR1 and its putative fragmentation scheme.
(D) Fragmentation pattern of [M-H]− ion of the reaction product of TKPR2 is identical to that of TKPR1 reaction product (C), thus indicating that both enzymes catalyze the reduction of the carbonyl function borne by the aliphatic chain of the tetraketide compound.