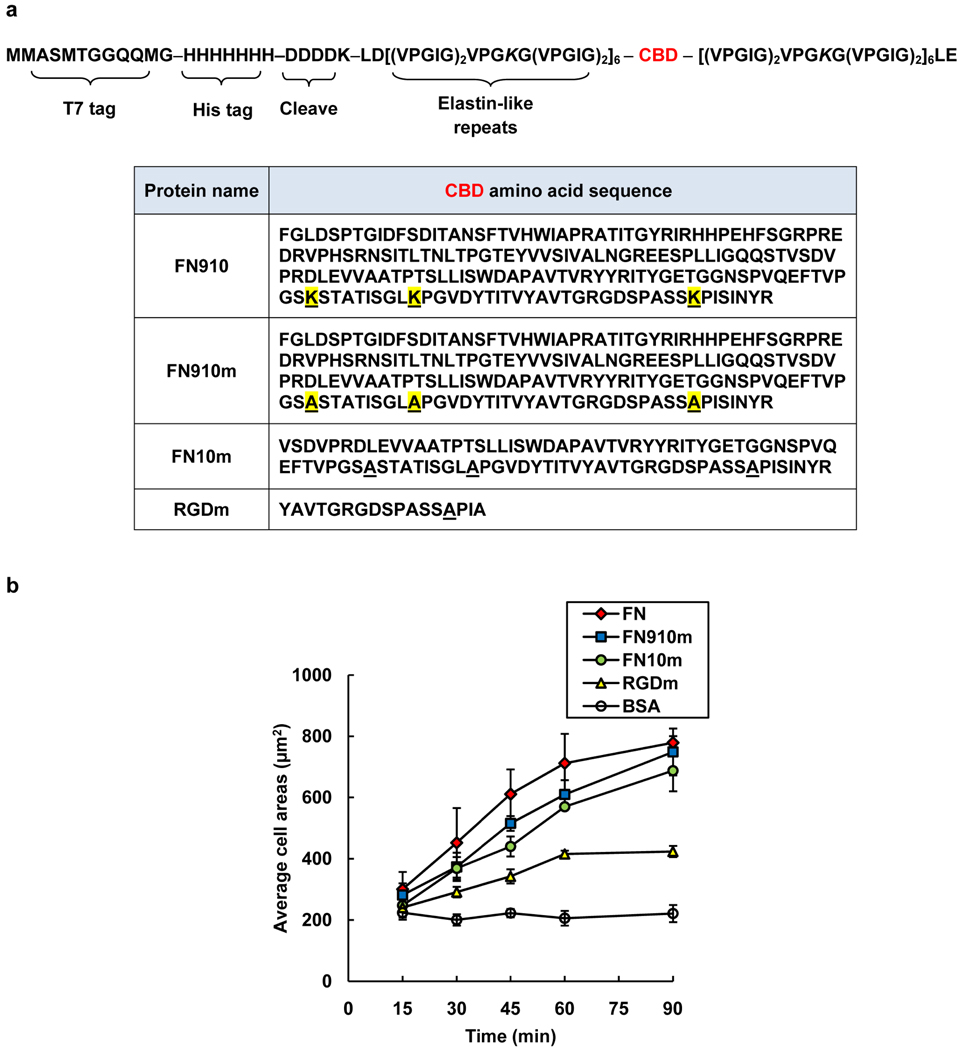
Figure 1.
Artificial extracellular matrix (aECM) proteins containing full-length fibronectin domains. a) The general amino acid sequence of the aECM proteins. Each protein contains an N-terminal T7 tag, a hepahistidine tag, and an enterokinase cleavage site followed by six elastin-like repeats, a cell-binding domain (CBD, see table) and six elastin-like repeats. The differences between FN910 and FN910m are highlighted in yellow. The letter “m” denotes cell-binding domains containing lysine-to-alanine mutations. b) The average projected cell areas for the adsorbed protein surfaces at each time point. Data represent means ± SEM from three independent experiments.