Abstract
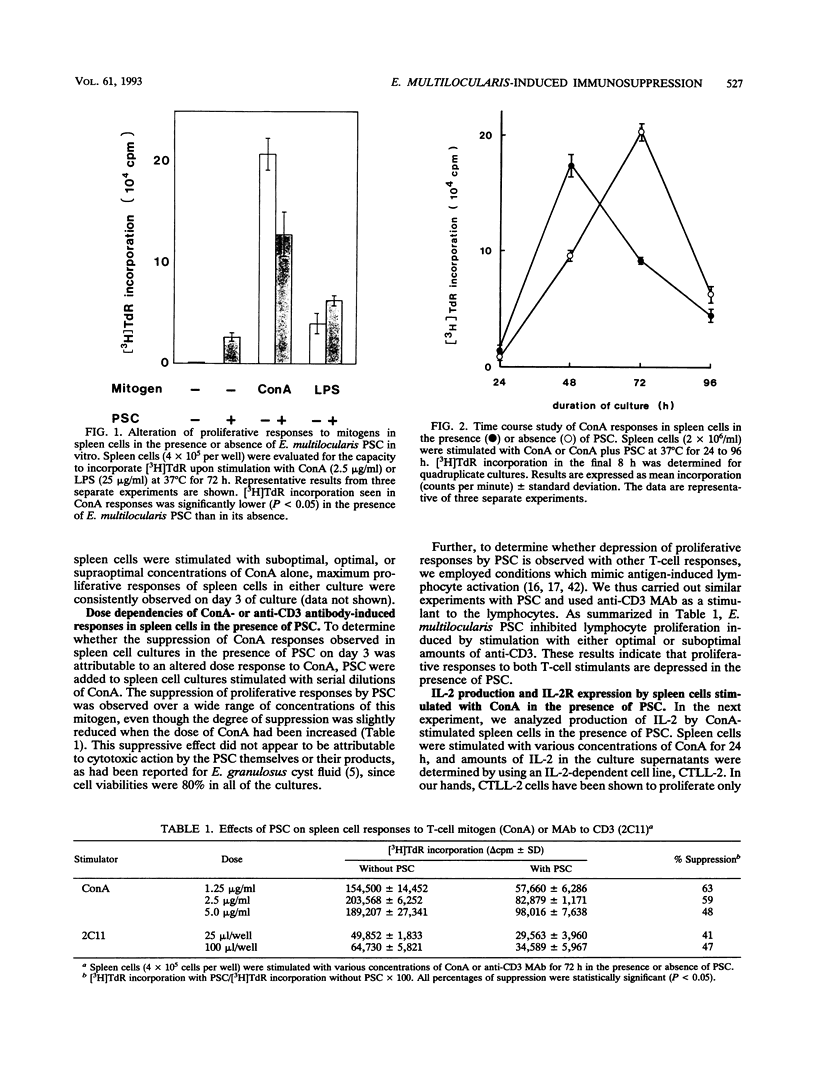
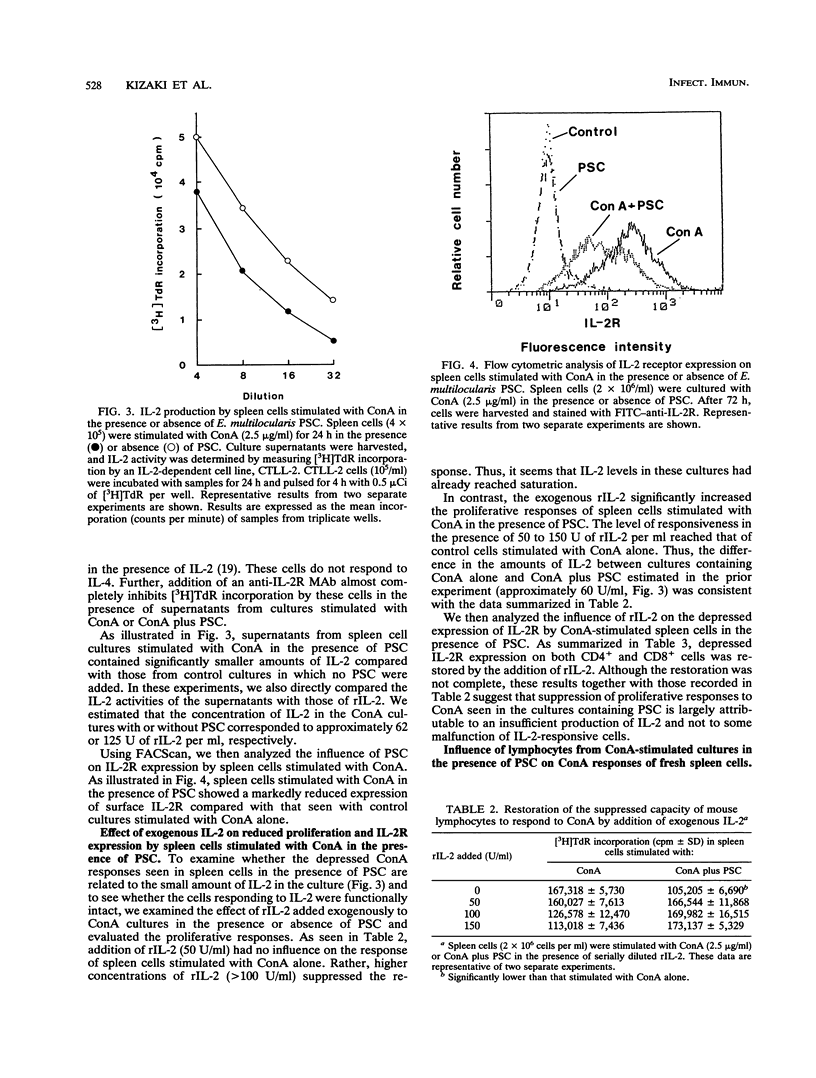
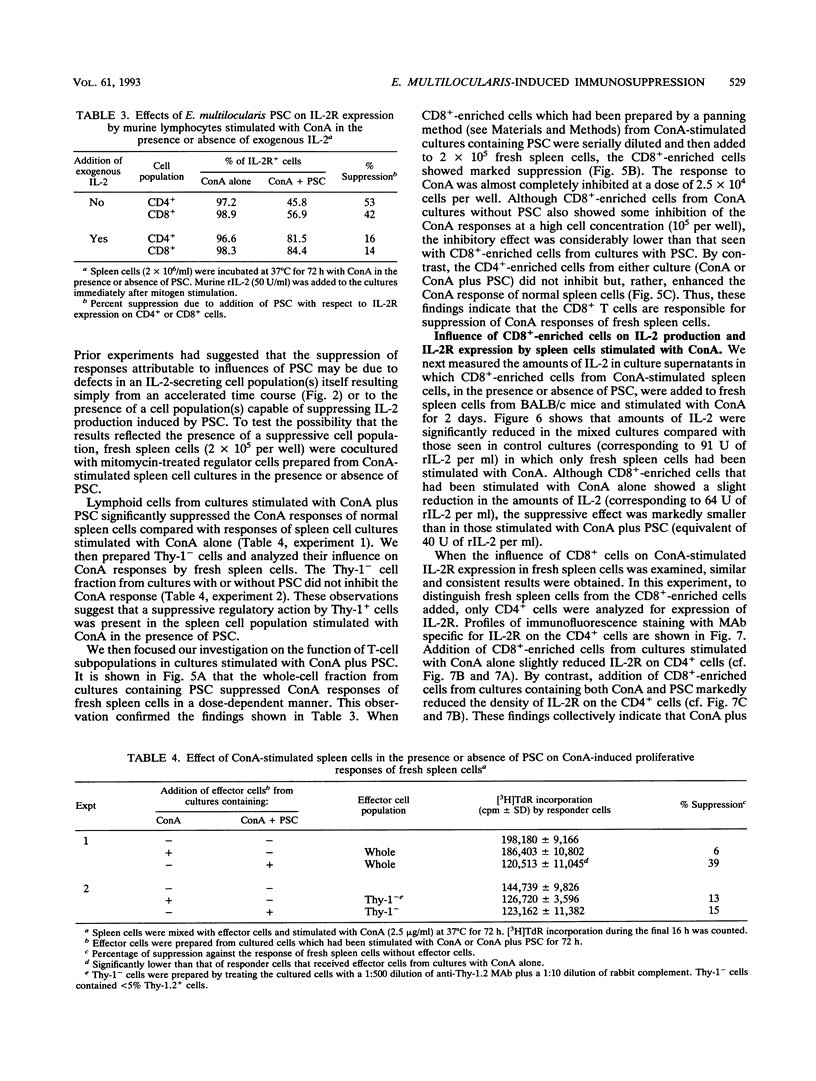
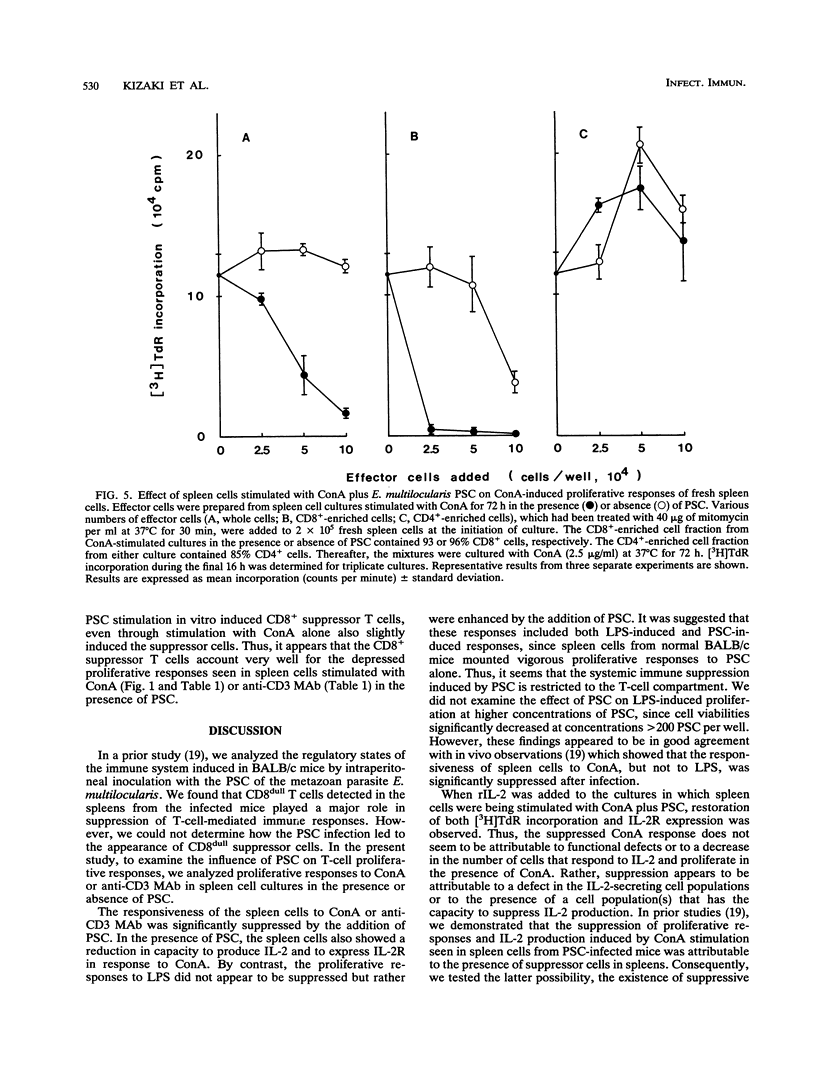
Immunoregulatory influences of protoscolices (PSC) of Echinococcus multilocularis on murine T-lymphocyte functions have been examined in an in vitro system. Proliferative responses of spleen cells stimulated with concanavalin A (ConA) or anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies were depressed by the addition of PSC. In the presence of PSC, both interleukin-2 (IL-2) production and IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) expression by lymphocytes stimulated with ConA were significantly reduced. However, exogenous IL-2 reconstituted both the ConA-stimulated proliferative responses and IL-2R expression. These findings suggest that PSC of E. multilocularis can suppress lymphoid cell responses via influences on IL-2 production. Indeed, addition of CD(8+)-enriched cells from cultures stimulated with ConA plus PSC to fresh spleen cells showed marked suppression of the ConA responses. IL-2 production as well as IL-2R expression on the spleen cells so treated were suppressed. These findings reveal a suppressive immunologic function induced by E. multilocularis PSC that involves inhibition of IL-2 production and reduction of IL-2R expression. The PSC-induced CD8+ cells appear to play a key role in the suppressive regulation of host immune responses against E. multilocularis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali-Khan Z. Cellular changes in the lymphoreticular tissues of C57L/J mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis cysts. Immunology. 1978 May;34(5):831–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Khan Z. Echinococcus multilocularis: cell-mediated immune response in early and chronic alveolar murine hydatidosis. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Dec;46(2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Khan Z., Siboo R. Pathogenesis and host response in subcutaneous alveolar hydatidosis. I. Histogenesis of alveolar cyst and a qualitative analysis of the inflammatory infiltrates. Z Parasitenkd. 1980;62(3):241–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00926565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkarmi T., Behbehani K. Echinococcus multilocularis: inhibition of murine neutrophil and macrophage chemotaxis. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jul;69(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annen J. M., Köhler P., Eckert J. Cytotoxicity of Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid in vitro. Z Parasitenkd. 1981;65(1):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00926556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R. W., Tanner C. E. The effect of immunosuppression on secondary Echinococcus multilocularis infections in mice. Int J Parasitol. 1976 Feb;6(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(76)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz L. A., Sztein M. B., Kierszenbaum F. Novel mechanism for Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of human lymphocytes. Inhibition of IL-2 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. Games parasites play: how parasites evade immune surveillance. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):21–26. doi: 10.1038/279021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Fradelizi D. The mechanism of inhibition of human IL 2 production. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2463–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. A., Smithers S. R. Death of schistosome cercariae during penetration of the skin. II. Penetration of mammalian skin by Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology. 1968 Feb;58(1):111–128. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000073479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Immune responses to a soluble schistosomal egg antigen preparation during chronic primary infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. J., Hall J. G., Targett G. A., Murray M. The biological significance of the immune response with special reference to parasites and cancer. J Parasitol. 1980 Oct;66(5):705–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. B., Jenkins P., Allan D. Immune recognition of Echinococcus granulosus. 1. Parasite-activated, primary transformation by normal murine lymph node cells. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Jan;4(1):33–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Jayawardena A. N. Suppressor cells in mice infected with Trypanosoma brucei. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Stobo J. D. Transmembrane signalling by the T cell antigen receptor. Perturbation of the T3-antigen receptor complex generates inositol phosphates and releases calcium ions from intracellular stores. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):446–456. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Weiss A., Stobo J. D. The antigen receptor on a human T cell line initiates activation by increasing cytoplasmic free calcium. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F. Immunologic deficiency during experimental Chagas' disease (Trypanosoma cruzi infection): role of adherent, nonspecific esterase-positive splenic cells. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2202–2205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizaki T., Kobayashi S., Ogasawara K., Day N. K., Good R. A., Onoé K. Immune suppression induced by protoscoleces of Echinococcus multilocularis in mice. Evidence for the presence of CD8dull suppressor cells in spleens of mice intraperitoneally infected with E. multilocularis. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1659–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeze W. K., Tanner C. E. Echinococcus multilocularis: susceptibility and responses to infection in inbred mice. Int J Parasitol. 1987 Apr;17(4):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(87)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammie P. J., Katz S. P. Immunoregulation in experimental filariasis. I. In vitro suppression of mitogen-induced blastogenesis by adherent cells from Jirds chronically infected with Brugia pahangi. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1381–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellouk S., Maheshwari R. K., Rhodes-Feuillette A., Beaudoin R. L., Berbiguier N., Matile H., Miltgen F., Landau I., Pied S., Chigot J. P. Inhibitory activity of interferons and interleukin 1 on the development of Plasmodium falciparum in human hepatocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4192–4195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa Y., Takada S., Ueda Y., Suzuki N., Hoshino T., Sakane T. Characterization of T lymphocyte subpopulations responsible for deficient interleukin 2 activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Ogawa H., Tsunematsu T. Isolation and characterization of a monoclonal nonspecific suppressor factor (MNSF) produced by a T cell hybridoma. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2904–2909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoé K., Iwabuchi K., Katsume C., Gotohda T., Arase A., Hatakeyama S., Mishima M., Good R. A., Ogasawara K. A study on graft-versus-host reaction (GVHR) by Simonsen's splenomegaly assay. Cells and antigen systems involved in induction of GVHR. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1989 Feb;39(2):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1989.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P. J., Phillips S. M. The molecular basis of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis. I. A T cell-derived suppressor effector factor. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1714–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Dodge G. R. Prostaglandin E inhibits the production of human interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):943–948. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Penta A. C., Hussey R. E., Schlossman S. F. A rapid method for separating functionally intact human T lymphocytes with monoclonal antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Nov;21(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich R. R., Pierce C. W. Biological expressions of lymphocyte activation. 3. Suppression of plaque-forming cell responses in vitro by supernatant fluids from concanavalin A-activated spleen cell cultures. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1360–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickard M. D., Williams J. F. Hydatidosis/cysticercosis: immune mechanisms and immunization against infection. Adv Parasitol. 1982;21:229–296. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley E. M., Dixon J. B. Experimental Echinococcus granulosus infection in mice: immunocytochemical analysis of lymphocyte populations in local lymphoid infections during early infection. Parasitology. 1987 Jun;94(Pt 3):523–532. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000055864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley E. M., Dixon J. B., Jenkins P., Ross G. Echinococcus granulosus infection in mice: host responses during primary and secondary infection. Parasitology. 1986 Apr;92(Pt 2):391–403. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000064155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley E. M., Dixon J. B., Kelly D. F., Cox D. A. The immune response to Echinococcus granulosus: sequential histological observations of lymphoreticular and connective tissues during early murine infection. J Comp Pathol. 1985 Jan;95(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(85)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Human suppressor T cells induced by concanavalin A: suppressor T cells belong to distinctive T cell subclasses. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. A., Farrell J. P. Experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. I. Nonspecific immunodepression in BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania tropica. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2395–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of IL-2 production. I. Evidence for the presence of IL-2-producing cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2763–2768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of IL-2 production. II. Evidence for a role for suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2769–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Andersson G., Stoczkowska M., Shabo R., Romero P., Patarroyo M. E., Wigzell H., Perlmann P. Production of IL 2 and IFN-gamma by T cells from malaria patients in response to Plasmodium falciparum or erythrocyte antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3498–3504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. F., Rausch R. L. Alveolar hydatid disease. A review of clinical features of 33 indigenous cases of Echinococcus multilocularis infection in Alaskan Eskimos. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Nov;29(6):1340–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


