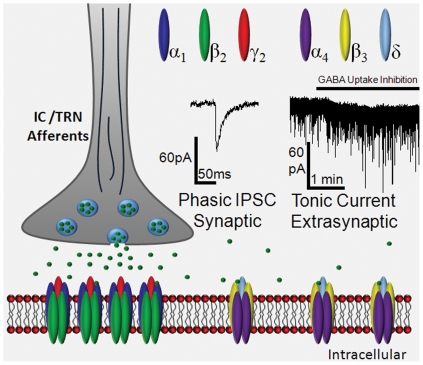
Figure 3. Summary Illustration of GABAARs on MGB Neurons:
Note receptor location relative to the presynaptic GABAergic terminal (IC or TRN) with classic α1γ-subunit containing GABAARs located within the synapse and α4δ-subunit containing GABAARs outside of the synapse. The concentration of GABA to which each receptor type is typically exposed and the nature of the current mediated by each subtype of receptor is also depicted. For sample traces, the internal solution used here is CsCl-based (140 mM) and the membrane potential is clamped at −60 mV. As a result, GABAAR currents are inward and blocked by gabazine. The phasic response (left trace) is expanded from within the trace of the tonic response (right trace). The inward shift in baseline current is induced by upregulating extracellular GABA through inhibition of GABA uptake via the application of neuronal and glial GABA transporters with NNC-711 and SNAP 5114, respectively (solid line, right trace). These sample recordings were obtained from an MGB neuron of a 7-month-old FBN rat.