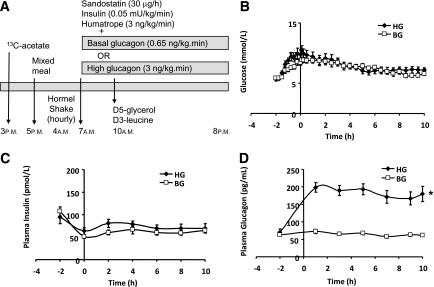
FIG. 1.
Study protocol (A) and plasma concentrations of glucose (B), insulin (C), and glucagon (D) over the time course of the study. A constant infusion of sodium 1-13C-acetate was started at 3 p.m. on the day before the kinetics study. A mixed meal was provided that day at 5 p.m., after which the subject fasted. At 4 a.m. the next day subjects started to ingest identical hourly, then half hourly, volumes of a liquid high fat nutritional supplement to maintain a constant fed state. At 7 a.m., i.e., 3 h after starting to ingest the formula, a pancreatic clamp was started with infusion of somatostatin, insulin, growth hormone, and glucagon, the latter to achieve either BG (□) or HG (♦) plasma concentrations. At 10 a.m. (referred to as time 0 for the lipoprotein kinetic study), i.e., 3 h after starting the pancreatic clamp, a bolus of [1,1,2,3,3-2H5]-glycerol (d5-glycerol) was administered and a primed, constant infusion of l-[5,5,5-2H3]-leucine (d3-leucine) was started and continued for 10 h (A). Plasma glucose (B) and insulin (C) concentrations were similar in BG and HG studies, whereas glucagon (D) was approximately threefold higher in HG vs. BG. *P < 0.0001 HG vs. BG.