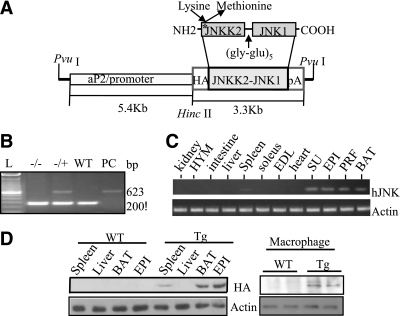
FIG. 1.
Generation and characterization of aP2-dn-JNK transgenic (Tg) mice. A: Schematic representation of the aP2-dn-JNK transgenic construct. The dn-JNK cDNA, in which lysine 149 in the ATP domain of the JNKK2 moiety was replaced by Met to create the HA-JNKK2(K149M)JNK1, was subcloned downstream of the 5.4-kb aP2 promoter/enhancer and upstream of the hGH polyadenylation signals. B: Detection of the dn-JNK transgene by PCR analysis in mice. Specific fragments of 653 bp spanning from the aP2 promoter to the JNKK2 gene was amplified. −/−, transgene negative; −/+, transgene positive; L, 1-kb DNA ladder; PC, plasmid DNA positive control; WT, wild-type littermates. C: Expression of the dn-JNK transgene by RT-PCR. The presence of the dn-JNK mRNA was analyzed in various tissues of aP2-dn-JNK transgenic mice (10 weeks old) by RT-PCR using specific primers for the dn-JNK transgene (n = 5). EPI, epididymal adipose fat; PRF, perirenal fat; SU, subcutaneous adipose fat. D: Confirmation of the dn-JNK protein expression by immunoblotting (n = 4). Protein extracts from various tissues were subjected to Western blotting with anti-HA antibody.