Abstract
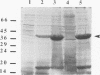
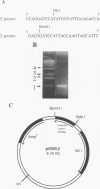
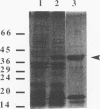
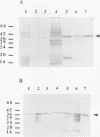
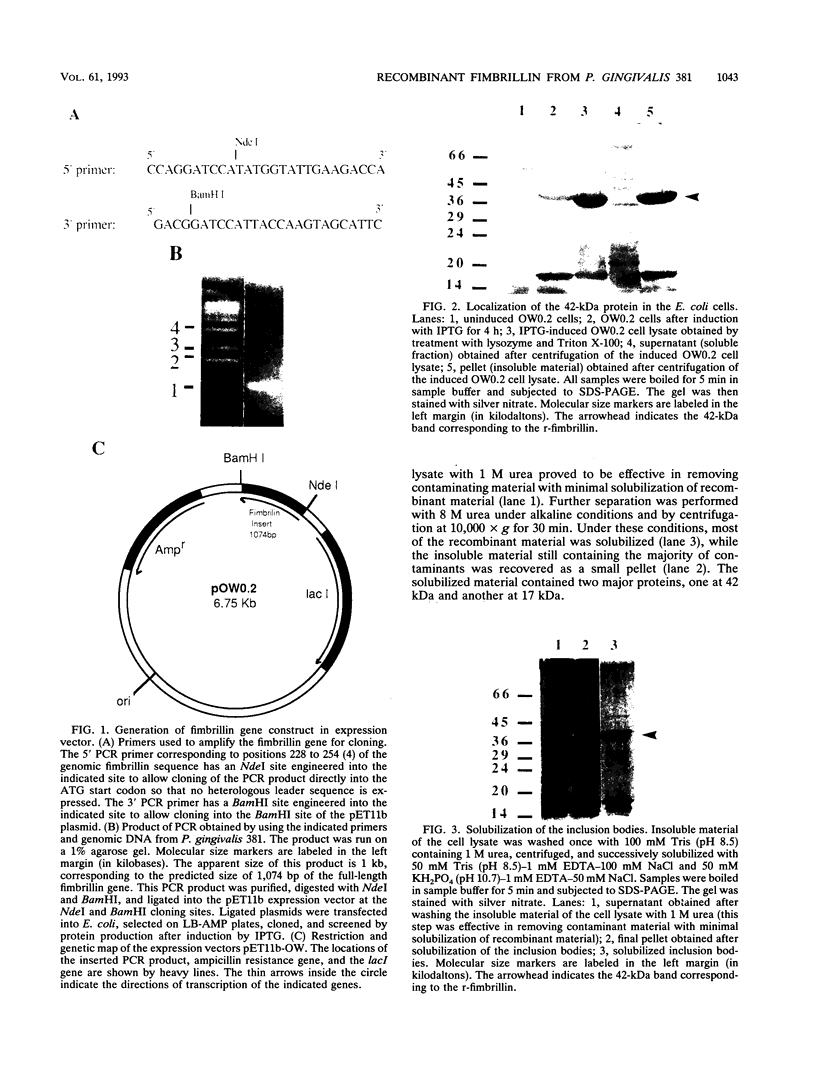
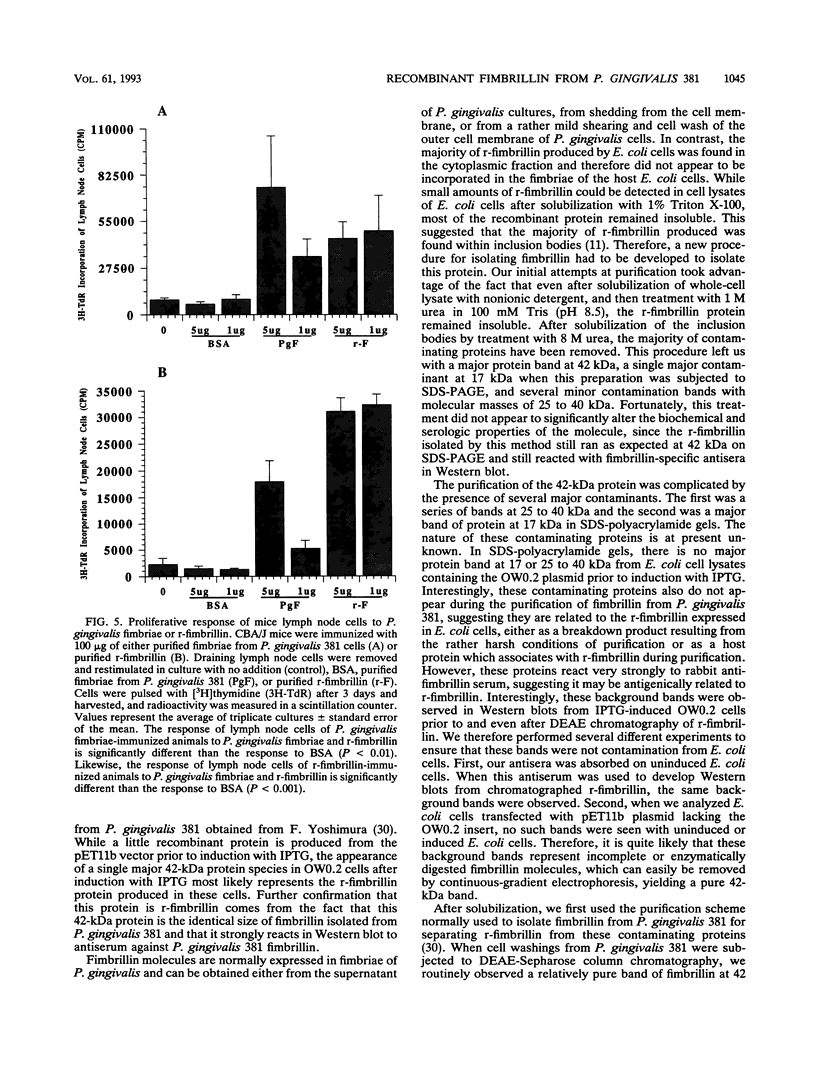
Fimbrillin is the major subunit protein of fimbriae from the human periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. We describe here the generation and initial characterization of recombinant fimbrillin (r-fimbrillin) isolated from P. gingivalis 381. A fragment of DNA encoding the gene for fimbrillin was generated by polymerase chain reaction and cloned into the expression vector pET11b. Plasmids containing the recombinant gene were transfected into Escherichia coli. Clones were selected on plates for ampicillin resistance and individually screened by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) for protein production after activation with IPTG (isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside). One clone, OW0.2, produced significant amounts of a 42-kDa protein after induction with IPTG. This clone contained the pET11b plasmid with a 1-kb insert that had sequence homology to the gene encoding fimbrillin. The majority of recombinant protein from clone OW0.2 was found in the cytoplasm within inclusion bodies. Protein aggregates were solubilized in 8 M urea, and SDS-PAGE analysis showed two major protein bands, one at 42 kDa and the other at 17 kDa. These two proteins coeluted from a DEAE-Sepharose column at 0.15 M NaCl and were reactive to rabbit antiserum to fimbrillin in a Western blot (immunoblot). A preparation giving a single protein band at 42 kDa in SDS-PAGE was obtained by size fractionation by using continuous-elution electrophoresis. Lymph node cells from animals immunized with either fimbrillin from P. gingivalis or r-fimbrillin showed antigen-specific proliferation to both P. gingivalis fimbrillin and r-fimbrillin in an in vitro recall assay. Therefore, it appears that r-fimbrillin is chemically, antigenically, and serologically identical to fimbrillin isolated from P. gingivalis 381.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W. Fast and sensitive detection of protein and DNA bands by treatment with potassium permanganate. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1985 May;11(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(85)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deslauriers M., Mouton C. Epitope mapping of hemagglutinating adhesion HA-Ag2 of Bacteroides (Porphyromonas) gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2791–2799. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2791-2799.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. P., Kubiniec M. A., Yoshimura F., Genco R. J. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the fimbrial subunit protein of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1658–1665. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1658-1665.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Klausen B., Sojar H. T., Bedi G. S., Sfintescu C., Ramamurthy N. S., Golub L. M., Genco R. J. Immunization with Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbriae protects against periodontal destruction. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2926–2935. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2926-2935.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne P. A., Ellen R. P. Evidence that Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbriae function in adhesion to Actinomyces viscosus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5266–5274. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5266-5274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanazawa S., Hirose K., Ohmori Y., Amano S., Kitano S. Bacteroides gingivalis fimbriae stimulate production of thymocyte-activating factor by human gingival fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):272–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.272-274.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isogai H., Isogai E., Yoshimura F., Suzuki T., Kagota W., Takano K. Specific inhibition of adherence of an oral strain of Bacteroides gingivalis 381 to epithelial cells by monoclonal antibodies against the bacterial fimbriae. Arch Oral Biol. 1988;33(7):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(88)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Sojar H. T., Bedi G. S., Genco R. J. Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis fimbrillin: size, amino-terminal sequence, and antigenic heterogeneity. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):383–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.383-389.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Ni Eidhin D., Deslauriers M., Lamy L. The hemagglutinating adhesin HA-Ag2 of Bacteroides gingivalis is distinct from fimbrilin. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Feb;6(1):6–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1991.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Kono Y., McGhee M. L., McGhee J. R., Roberts J. E., Hamada S., Kiyono H. Porphyromonas gingivalis-specific serum IgG and IgA antibodies originate from immunoglobulin-secreting cells in inflamed gingiva. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):237–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Kusumoto Y., Uchida H., Nagashima S., Ogo H., Hamada S. Immunobiological activities of synthetic peptide segments of fimbrial protein from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1335–1341. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Shimauchi H., Kusumoto Y., Hamada S. Humoral immune response to Bacteroides gingivalis fimbrial antigen in mice. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):8–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Yamamoto A., Naito Y., Takazoe I., Slots J., Genco R. J. Purification and properties of hemagglutinin from culture supernatant of Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):659–665. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.659-665.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E., Loeb M., Anderson, Smith D. H. Do pili play a role in pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type B? Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelan R. S., Grossman L. I. A rapid protocol to isolate DNA fragments from low melting temperature agarose. Biotechniques. 1991 Feb;10(2):186–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sojar H. T., Lee J. Y., Bedi G. S., Cho M. I., Genco R. J. Purification, characterization and immunolocalization of fimbrial protein from Porphyromonas (bacteroides) gingivalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91624-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I., Nakamura T., Okuda K. Colonization of the subgingival area by Bacteroides gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):422–426. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Boslego J. W., Ciak J., McChesney D., Brinton C. C., Wood S., Takafuji E. Gonococcal pilus vaccine. Studies of antigenicity and inhibition of attachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):881–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI110343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Sugano T., Kawanami M., Kato H., Suzuki T. Detection of specific antibodies against fimbriae and membrane proteins from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis in patients with periodontal diseases. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(9):935–941. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Takahashi K., Nodasaka Y., Suzuki T. Purification and characterization of a novel type of fimbriae from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):949–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.949-957.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Takasawa T., Yoneyama M., Yamaguchi T., Shiokawa H., Suzuki T. Fimbriae from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis: physical, chemical, and immunological properties. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):730–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.730-734.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]