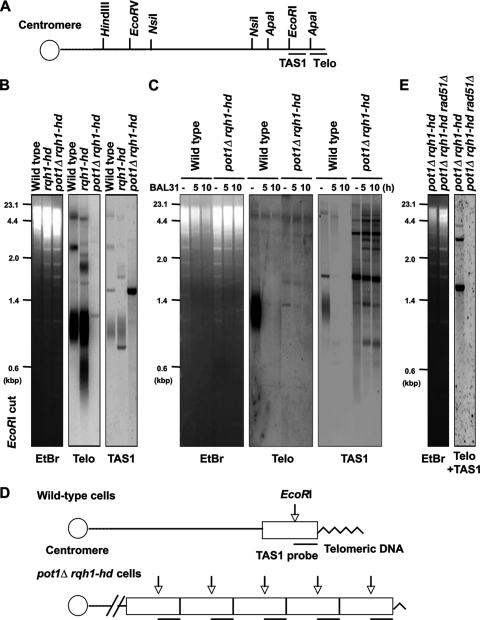
FIG. 2.
pot1Δ rqh1-hd double mutant can maintain telomeres that are dependent on HR activity. (A) Restriction enzyme sites around the telomeric (Telo) and telomere-associated sequence (TAS1) of 1 chromosome arm cloned in the plasmid pNSU70 (37). (B) The telomere length of the wild-type, rqh1-hd, and pot1Δ rqh1-hd cells was analyzed using Southern hybridization at 25°C. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI, separated by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, and hybridized to a 450-bp synthetic telomere fragment as a probe, or a 700-bp DNA fragment containing the TAS1 sequence. To assess the total amount of DNA, the gel was stained with ethidium bromide (EtBr) before blotting onto the membrane. (C) BAL31 nuclease treatment of genomic DNA from wild-type and pot1Δ rqh1-hd cells. Samples were digested with 4 units of BAL31 nuclease (NEB) for 5 or 10 h. After the BAL31 treatment, genomic DNA was analyzed as described for panel B. (D) Schematic diagram of telomeric structure in wild-type and pot1Δ rqh1-hd cells. Telomeric sequences are indicated as zigzag line. TAS1-containing subtelomeric elements are indicated as a box. Vertical arrows indicate the position of EcoRI digestion. The canonical positions of TAS1 sequence are indicated by line below the box. (E) The telomere lengths of the pot1Δ rqh1-hd cells and pot1Δ rqh1-hd rad51Δ cells were analyzed using Southern hybridization at 25°C. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized to a 1-kbp DNA fragment containing telomere plus TAS1 sequences.