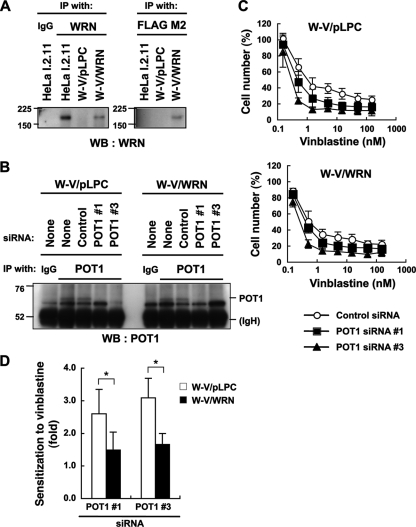
FIG. 7.
POT1 and WRN deficiencies render human cultured cells sensitive to vinblastine. (A) Establishment of the cell lines. WRN-deficient W-V cells were infected with the retrovirus for FLAG-tagged WRN (W-V/WRN). W-V/pLPC is a mock infectant used as the control. The TNE lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP), followed by Western blot analysis (WB). HeLa I.2.11 cells were used as a control for the detection of endogenous WRN. IgG, normal immunoglobulin G. Values indicate the protein size markers (in thousands). (B) POT1 depletion using siRNA. The cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA. After a 48-h incubation, the TNE lysates were subjected to IP, followed by Western blot analysis. IgH, immunoglobulin heavy chain. (C) Effects of POT1 and WRN deficiencies on the sensitivity to vinblastine, an inhibitor of microtubule polymerization. The cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA for 24 h and then incubated with various concentrations of vinblastine for 48 h. Cell number (%) refers to the cell counts normalized to those in the absence of vinblastine. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of 3 or 4 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. (D) Reconstitution of WRN counteracts the POT1 knockdown-induced sensitization to vinblastine in W-V cells. Sensitization to vinblastine (ratio of IC50 values of control siRNA-treated cells to those of POT1 knockdown cells) was determined from the data shown in panel C. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of 3 or 4 independent experiments. Asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05).