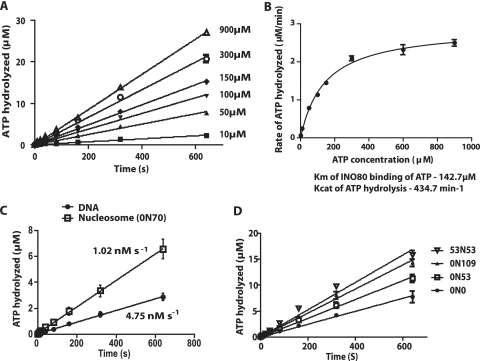
FIG. 4.
The ATPase activity of INO80 is enhanced with increasing lengths of extranucleosomal DNA. (A) The rate of ATP hydrolysis by INO80 with 0N70 nucleosomes was measured with different concentrations of ATP (10 to 900 μM). Nucleosomes (33 nM) were prebound with INO80 (6.67 nM) for 15 min at 30°C before addition of ATP. The amount of ATP hydrolyzed at different time points was determined using thin-layer chromatography, and ATP hydrolyzed (in μM) versus time (in seconds) was plotted for the different ATP concentrations. (B) The Km and Kcat values for INO80 were determined by plotting the rate of ATP hydrolyzed (in μM min−1) versus the concentration of ATP, with nonlinear fitting to the Michaelis-Menten equation using GraphPad. (C) The rates of ATP hydrolysis of INO80 with DNA or nucleosomes were determined as for panel A with 80 μM ATP. The free DNA used was the same DNA used to reconstitute the 0N70 nucleosomes. (D) The effects of extranucleosomal DNA length on the rate of ATP hydrolysis by INO80 were examined using nucleosome core particle (0N0), or 53 or 109 bp of extranucleosomal DNA at only one entry site (0N53 and 0N109), or with 53 bp of extranucleosomal DNA at both entry sites (53N53). The assays were performed as described for panel A, except with a fixed concentration of 80 μM ATP. In all of these reactions, only PCR-generated DNA was used.