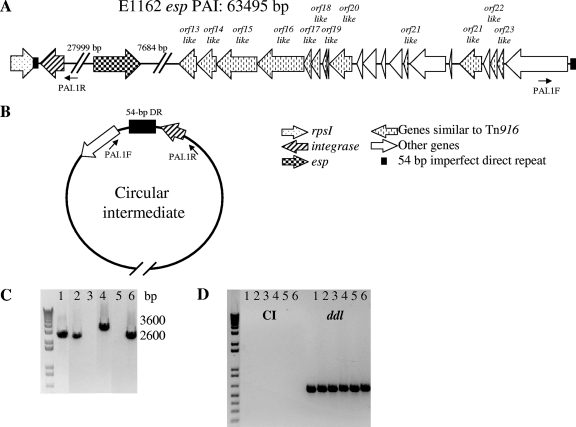
FIG. 1.
(A) Structure of the E. faecium E1162 esp PAI. Arrows indicate coding sequences (CDS) and direction of transcription; only CDS that are relevant for this study are depicted. Indicated are binding sites for the outward-facing primers (PAI.1R and PAI.1F) used to detect circular intermediates. (B) A schematic representation of circular intermediate (CI) formation. Primers (PAI.1R and PAI.1F) for the detection of circular intermediates are indicated. (C) Detection of circular intermediates using inversed PCR analysis on purified chromosomal DNA with outward-facing primers at the borders of the esp PAI. (D) Detection of circular intermediates using inversed PCR analysis on purified chromosomal DNA after S1 nuclease treatment; ddl PCR analysis was performed as a positive control. Lanes: 1, conjugation mixture of E. faecium strain E1162Δesp with BM4105RF; 2, E1162; 3, E1162ΔintA; 4, E1162ΔintA::pEF30; 5, E1162ΔintA::pEF25; and 6, the transconjugant (TC).