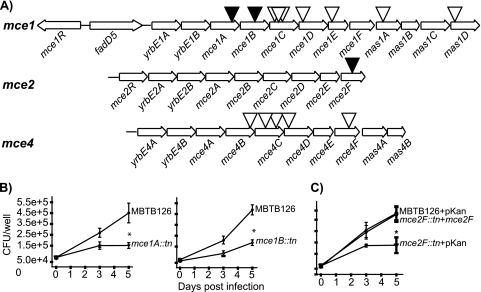
FIG. 2.
Evaluation of M. tuberculosis mce::Tn′blaTEM-1 mutants in macrophages. (A) Representation of mce1, mce2, and mce4 operons in M. tuberculosis H37Rv. Black triangles indicate Tn′blaTEM-1 insertion mutants with macrophage growth defects. White triangles mark Tn′blaTEM-1 insertion mutants that were not attenuated. The mce1 operon has two possible start sites and spans from either fadD5 or yrbE1A to mas1D (12, 20). The mce2 and mce4 operons are transcribed in a single transcript comprised of the genes shown (11, 24). (B) Murine bone marrow-derived macrophages were infected with M. tuberculosis MBTB126, the mce1A::Tn′blaTEM-1 mutant, or the mce1B::Tn′blaTEM-1 mutant. At 4 h (day 0) and 3 and 5 days postinfection, macrophages were lysed and plated to enumerate intracellular bacteria. Error bars indicate standard deviations (SD) of the means. (C) MBTB126 carrying pMV261.kan, the mce2F::Tn′blaTEM-1 mutant carrying pMV261.kan, and the mce2F::Tn′blaTEM-1 mutant carrying a multicopy complementing vector expressing mce2F from a constitutive promoter (pJES153) were used to infect macrophages as described for panel B. *, P ≤ 0.05. Each graph shows representative data from one of at least three independent replicate experiments.