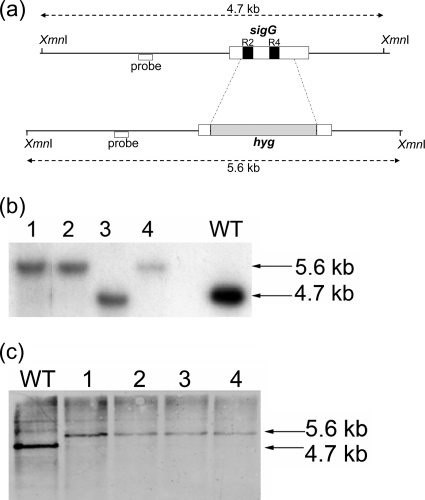
FIG. 2.
Construction of sigG mutant strains. (a) A total of 691 bp internal to sigG was deleted by allelic recombination and replaced with a 1.6-kb hygromycin cassette. The schematic shows the locations of the regions replaced within sigG (dotted lines) and the DNA binding regions 2.4 (R2) and 4.2 (R4) (black boxes). The positions of the probes (white boxes below lines) and XmnI restriction sites used in Southern blot analysis are indicated, along with the expected fragment sizes detected in the wild-type and mutant strains (double-headed arrows). (b and c) Genomic DNA was extracted from potential ΔsigG mutant colonies (lanes 1 to 4) and Southern blot analysis of the genomic DNA performed alongside wild-type DNA analysis (lanes WT) after digestion was performed with XmnI and either a radiolabeled probe (b) or a horseradish peroxidase-labeled probe (c) used to detect potential double crossovers. (b) ΔsigG1 mutant construction; colonies 1, 2, and 4 showed the correct genotype. (c) ΔsigG2 mutant construction; all 4 colonies showed the correct genotype.