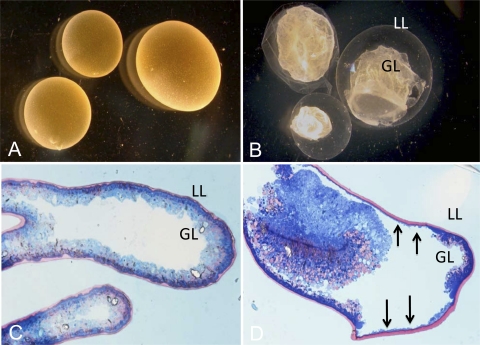
FIG. 1.
Morphological effects of mefloquine treatment on metacestodes. In vitro-cultivated E. multilocularis metacestodes were kept either in normal cultivation medium (A and C) or in medium containing 24 μM mefloquine (B and D) for 4 to 6 h. Macroscopical pictures (A and B) show the dramatic morphological changes of metacestodes upon treatment: The germinal layer (GL) detaches rapidly from the laminated layer (LL). Upon methylene-blue/basic fuchsin staining of Epon-embedded parasites (C and D), the separation of the GL and LL was further confirmed. The residual GL, still attached to the LL but strongly reduced in thickness, is indicated by arrows.