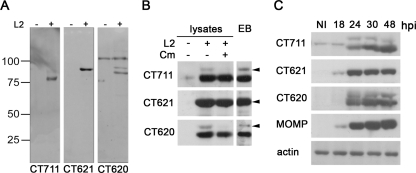
FIG. 3.
Expression of the C. trachomatis DUF582 proteins CT711, CT620, and CT621 during chlamydial infection. (A) Polyclonal antiserum obtained after immunization of rabbits with recombinant CT711, CT620, and CT621 was tested for its specificity on whole-cell lysates. HeLa cells were mock infected (−) or infected with C. trachomatis L2 (+) for 30 h. Total cell lysates were resolved in polyacrylamide gels and probed by immunoblotting with antibodies to CT711, CT620, and CT621. (B) HeLa cells were infected or not with C. trachomatis L2 for 40 h at 37°C, prior to addition of 100 μg/ml chloramphenicol (Cm) in the indicated sample. Ninety minutes later, the cells were collected and whole-cell lysates were probed with the indicated antibodies. Density gradient-purified EBs were lysed and run in parallel with the whole-cell lysates. Arrowheads point to the expected molecular size for each DUF582 protein. (C) HeLa cell lysates infected with C. trachomatis L2 for the indicated time were run on SDS-PAGE and transferred to membranes. Membranes were probed with antibodies to CT711, CT621, CT620, and MOMP. Antibodies against actin were used as a loading control.