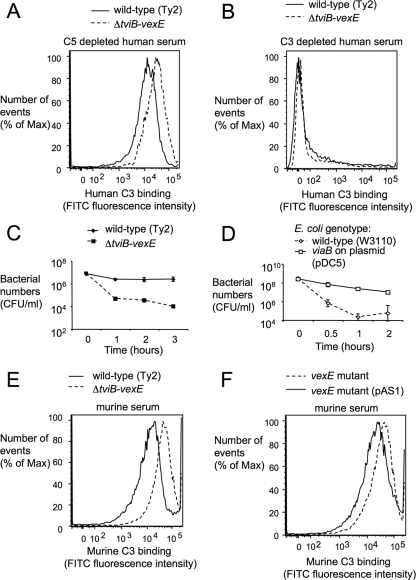
FIG. 2.
The Vi capsule reduces C3 fixation and increases complement resistance. (A and B) Fixation of C3 after incubation of capsulated (wild-type) and noncapsulated (ΔtviB-vexE) S. Typhi strains in C5-depleted human serum (A) or in C3-depleted human serum (B) detected by flow cytometry using an anti-human C3 FITC conjugate. (C and D) Survival of capsulated and noncapsulated S. Typhi strains (C) or capsulated (viaB on plasmid pDC5) and noncapsulated (wild-type [W3110]) E. coli strains (D) in normal human serum. The experiment was repeated three times independently, and data points represent averages ± standard deviations. (E) Fixation of C3 after incubation of capsulated and noncapsulated S. Typhi strains in murine serum detected by flow cytometry using an anti-murine C3 FITC conjugate. (F) Fixation of C3 after incubation of capsulated (vexE mutant complemented with pAS1) and noncapsulated (vexE mutant) S. Typhi strains in murine serum detected by flow cytometry using an anti-murine C3 FITC conjugate. The experiments whose results are presented in panels A, B, E, and F were repeated three times independently with similar outcomes each time, and a representative examples are shown.