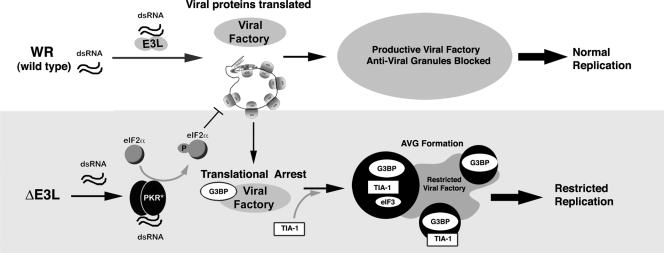
FIG. 8.
Model of the role of AVGs in the antiviral response to VV. Infection with WT virus (top) produces dsRNA, which is bound by E3L, preventing PKR activation and leading to a productive infection as eIF2α phosphorylation and AVG formation are suppressed by E3L. Infection with ΔE3L mutant virus (bottom) results in PKR activation, leading to eIF2α phosphorylation and delayed translation initiation. Factory-associated viral mRNAs are bound by the translational silencer TIA-1, which restricts viral replication. Abundant AVGs containing mRNA, G3BP, TIA-1, and associated proteins form.