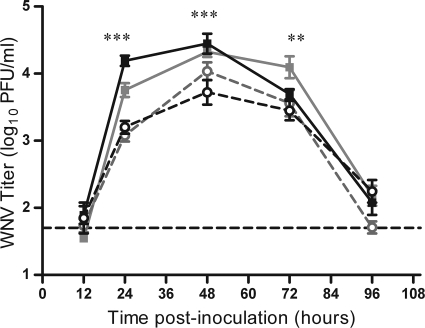
FIG. 4.
Spot feeding causes higher early viremia in mice. Mice were needle inoculated s.c. with 105 PFU of WNV-C6/36 in the left rear footpad without mosquito exposure (dashed lines, open symbols) or in the left rear footpad at a spot where up to 5 uninfected C. tarsalis mosquitoes had probed and/or fed (spot feeding) (solid lines, filled symbols). Serial serum samples were harvested at various times postinoculation, and plaque assays were performed. Two replicates of this experiment were performed (n = 8 to 16 mice per group per time point). Black lines indicate data from the 1st replicate, and gray lines indicate data from the 2nd replicate. A two-way ANOVA was performed on ranked data to determine effect of treatment and replicate. Significant treatment effect P values are indicated as follows: **, P = 0.001 to 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. A significant replicate effect was observed at 24 hpi (P = 0.001 to 0.01), and a significant treatment by replicate effect was observed at 48 hpi (P = 0.01 to 0.05). Error bars represent standard errors of the means. The horizontal dashed line indicates an LOD of 50 PFU/ml.