FIG. 1.
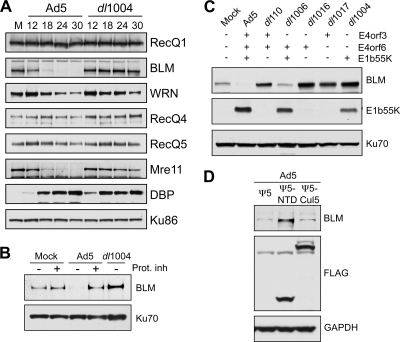
Adenovirus infection induces proteasome-mediated degradation of BLM. (A) The steady-state levels of cellular RecQ helicases were examined over a time course of adenovirus infection. HeLa cells were either mock infected (M) or infected with wild-type Ad5 (multiplicity of infection [MOI] of 10) or the E4-deleted mutant dl1004 (MOI of 25). Cells were harvested at the indicated hours postinfection (hpi) for analysis by immunoblotting (14). Specific antibodies were used to detect RecQ1 (Santa Cruz), WRN (BD Biosciences), RecQ4 (Cell Signaling), and RecQ5 (gift from P. Janscak) (32). To generate the anti-BLM antibody, rabbits were immunized with a purified recombinant protein consisting of a His-tagged BLM fragment (amino acid residues 1 to 439). The purified anti-BLM antiserum (designated 7099) was tested for specificity by immunoblotting and immunofluorescence (data not shown). The viral DBP (detected with monoclonal antibody B6, from A. Levine) served as a control for infection, and degradation of cellular proteins was confirmed by inclusion of the Mre11 positive control (Genetex). Antibody to Ku86 (Santa Cruz) served as a loading control. Although the levels of WRN were slightly affected, only BLM was reduced in an E4-dependent manner analogous to Mre11 degradation. (B) BLM degradation is proteasome dependent. Cells were infected with Ad5 (MOI of 10) or dl1004 (MOI of 25), and at 12 hpi, proteasome inhibitors (Prot. inh) (10 μM MG132 and 1 μM epoxomicin) were added to the cells for a further 12 h. Degradation of BLM by Ad5 was prevented by the proteasome inhibitors. Ku70 served as a loading control. (C) E1b55K and E4orf6 are required for degradation of BLM during adenovirus infection. BLM levels were compared in HeLa cells infected for 24 h with wild-type Ad5 or mutants lacking genes from the E1 and E4 regions as indicated (2, 10, 11, 26). Compared with results for mock-infected cells, BLM levels were reduced only during infection with viruses that express both E1b55K and E4orf6. E1b55K (detected with monoclonal antibody 2A6, from A. Levine) and Ku70 (antibody from Santa Cruz) served as controls for infection and gel loading, respectively. (D) The Cul5 complex is required for BLM degradation. Cells were infected with Ad5 (MOI of 10), superinfected (MOI of 50) with Ψ5, Ψ5-Cul5, or Ψ5-NTD (68), and harvested at 24 h after the primary infection. In these infections, the FLAG antibody (Sigma) demonstrates expression of Cul5 or NTD-Cul5 from the Ψ5 viruses, and GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) (Research Diagnostics Inc.) serves as a loading control.