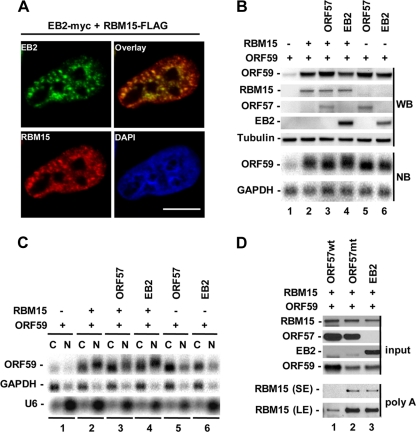
FIG. 11.
EBV EB2 does not prevent RBM15-mediated nuclear accumulation of ORF59 RNA and does not block RBM15-RNA interactions. (A) Colocalization of EB2-myc and RBM15-FLAG in HeLa cells by cotransfection. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B and C) EB2 promotes ORF59 expression but does not prevent RBM15-mediated nuclear accumulation of ORF59 RNA. HEK293 cells (2.5 × 105 cells/ml) were transfected with 300 ng of ORF59-FLAG with or without 20 ng RBM15-FLAG in addition to 100 ng empty vector, ORF57-FLAG, or EB2-myc. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were collected for total protein and RNA analyses by Western blot (WB) and Northern blot (NB) assays, respectively (B). Fractionated cytoplasmic and nuclear RNA was also analyzed in Northern blot assays by using a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probe specific for ORF59 RNA (C). (D) EB2 does not prevent RBM15's association with polyadenylated RNAs. HEK293 cells (5 × 105) were transfected with 500 ng each of ORF59-FLAG and RBM15-FLAG vectors together with 500 ng of an empty FLAG vector, ORF57-FLAG, or EB2-myc. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were exposed to UV light and polyadenylated RNAs were isolated. RBM15 proteins bound onto polyadenylated RNAs were analyzed by Western blotting. SE, short exposure; LE, long exposure.