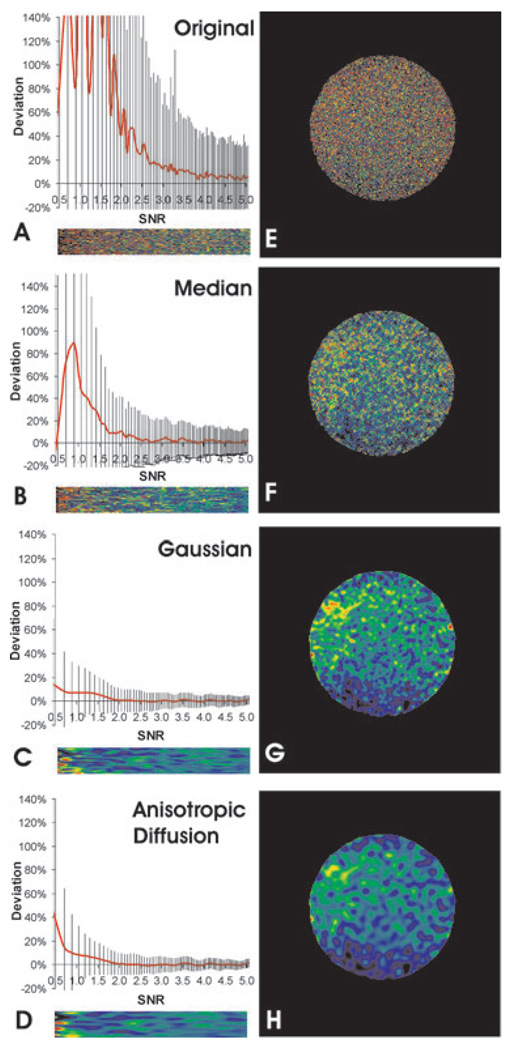
Fig. 4.
Restoration of ratio images with conventional noise reduction filters. Noisy grey scale (A–D) or bead images (SNR of denominator image about 2.6 before noise reduction; E–H) are shown without denoising (A, E), or after noise reduction with a median filter (B, F), Gaussian filter (C, G), or anisotropic diffusion filter (D, H) before taking the ratio. Systematic error relative to the correct value is calculated for the grey-scale images as a function of initial SNR between 0.5 and 5.0 (A–D plots). Vertical lines indicate the standard deviation. The corresponding ratio image is rendered in pseudo-colour and enlarged horizontally to match the scale shown in the graph. Pseudo-colour rendering is performed according to the colour scale shown in Fig. 3. Note the dramatic restoration of average intensity ratios towards correct values, which should be blue–green in pseudo-colour for both types of images as shown in Fig. 3(A). However, although Gaussian and anisotropic diffusion filters show better restoration of ratio than the median filter, both create artefacts of discrete ratio domains.