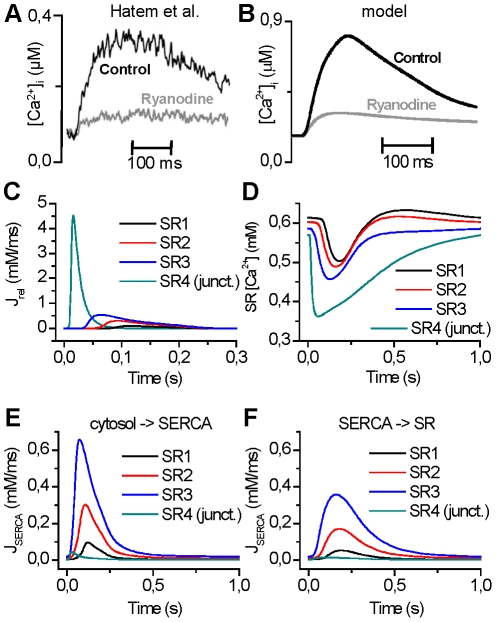
Figure 4. SR Ca2+ dynamics of the model.
(A) and (B) Inhibition of the SR Ca2+ release with ryanodine greatly reduces the Ca2+ transient amplitude in both experiments [7] and simulations. Detailed analysis indicates that the SR Ca2+ release generates 77% of the Ca2+ transient amplitude, which is in line with the experimental findings 79±6% of Hatem et al. [7]. (C) and (D) Most of the Ca2+ release is generated from the junctional compartment. (E) and (F) During the uptake of Ca2+ from the cytosol to the SR, the SERCA buffers the Ca2+ and generates a delay in the fluxes between the cytosol to SERCA and SERCA to SR. At the end of the diastolic phase, there is some diffusion of Ca2+ in the SR, which balances the concentration differences in different parts of the SR.