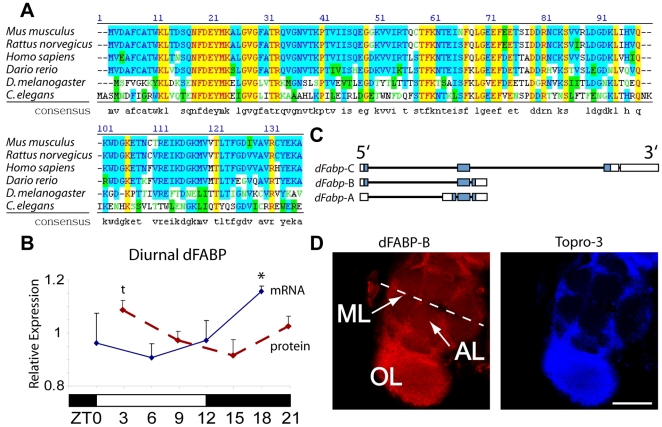
Figure 1. Characterization and diurnal regulation of the Drosophila fatty-acid binding protein, dFabp.
(A) Amino acid sequence homology of dFabp is compared to brain-type fatty-acid binding protein (Fabp7) of mouse, rat, human, zebra fish, and worm (lbp-7). A consensus sequence of all species is also shown. (B) Densitometric analysis of Northern and Western blots reveals a diurnal regulation of dFabp mRNA (blue solid line) and protein (red dashed line) in fly head. dFabp mRNA levels are normalized to Gapdh, with elevated expression during the sleep period (mean ± s.e.m., N = 2/timepoint, 50–100 heads per timepoint, asterisk P<0.05, t-test ZT18 vs ZT6). dFabp protein levels are normalized to laminin, and are elevated toward wake onset (mean ± s.e.m., N = 4/timepoint, 50–100 heads per timepoint, t P = 0.051, t-test ZT3 vs ZT15). Open bar = lights on, filled bar = lights off. (C) Schematic representation of the dFabp locus. Open bar = non-coding, filled bar = coding region. (D) Projection slice of brain stained with an antibody against dFabp (red), and the nuclear stain Topro-3 (blue), as viewed by confocal microscopy. ML = midline, OL = optic lobe, AL = antennal lobe, scale bar = 120 mm.