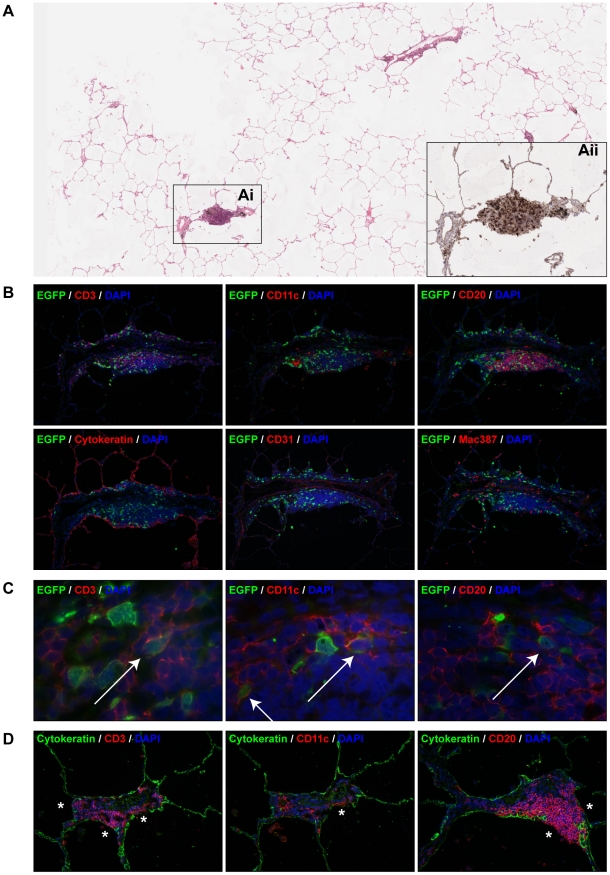
Figure 4. Characterization of MV infection in BALT structures.
(A) H&E staining on lung slice from an animal euthanized on 3 d.p.i.. The number of EGFP+ foci was extremely low, the boxed area (Ai) is a BALT which was the only area on the section where EGFP+ cells were present. (Aii) shows a serial section stained with anti-GFP (black) to detect the presence of virus (see also Figure S3, annotated immunohistochemical and H&E annotated pathology scans). (B) Indirect dual immunofluorescence of the infected BALT structure, showing the presence of T-lymphocytes (CD3), DC or macrophages (CD11c, mac387) and B-lymphocytes (CD20) within the BALT. The BALT is lined by a layer of cytokeratin-positive epithelial cells, and has a blood vessel with CD31-positive endothelium running through it transversely. (C) Higher magnifications of dual immunofluorescence within the BALT indicates the presence of MV-infected T-lymphocytes (CD3), DC or macrophages (CD11c) and B-lymphocytes (CD20), Double positive cells are indicated by arrows. In panel (B) and (C), EGFP+ cells are shown in green, cell-type specific staining is shown in red. DAPI was used to counter stain nuclei in blue. (D) Dual immunofluorescence performed on uninfected BALT region. Dual labelling with cytokeratin (green) and CD3, CD11c or CD20 (red) showed that T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes and DC or macrophages are present in very close proximity or in direct contact with the alveolar or bronchiolar lumen (asterisks). Single colour images for (C) are available as supporting data (figure S2).