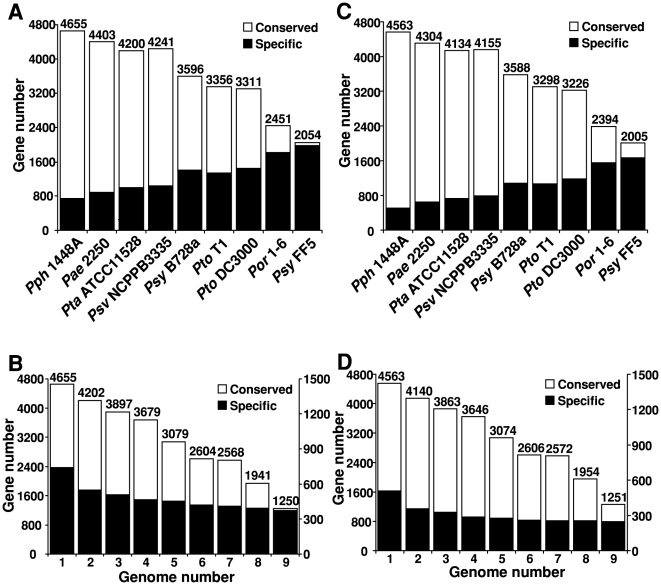
Figure 7. Numbers of conserved and specific genes in Psg genomes compared to nine Pseudomonas syringae genomes individually or by combination of genomes.
(A) Numbers of conserved and specific genes in Psg B076 compared to each of nine pseudomonad strains as described in Figure 6; (B) Numbers of conserved and specific genes in Psg B076 compared to combinations of nine pseudomonads based on results in (A) from left to right., i.e. “1” stands for one genome of Pph 1448A, “2” stands for two genomes (Pph 1448A and Pae 2250), “3” stands for three genomes (Pph 1448A, Pae 2250 and Pta ATCC 11528), and so on; (C) Numbers of conserved and specific genes in Psg race 4 compared to each of nine pseudomonad strains as described in Figure 6; (D) Numbers of conserved and specific genes in Psg race 4 compared to combinations of nine pseudomonads based on results in (C) from left to right., i.e. “1” stands for one genome of Pph 1448A, “2” stands for two genomes (Pph 1448A and Pae 2250), “3” stands for three genomes (Pph 1448A, Pae 2250 and Pta ATCC 11528), and so on. Numbers on the right Y-axis are for the specific genes in B and D.