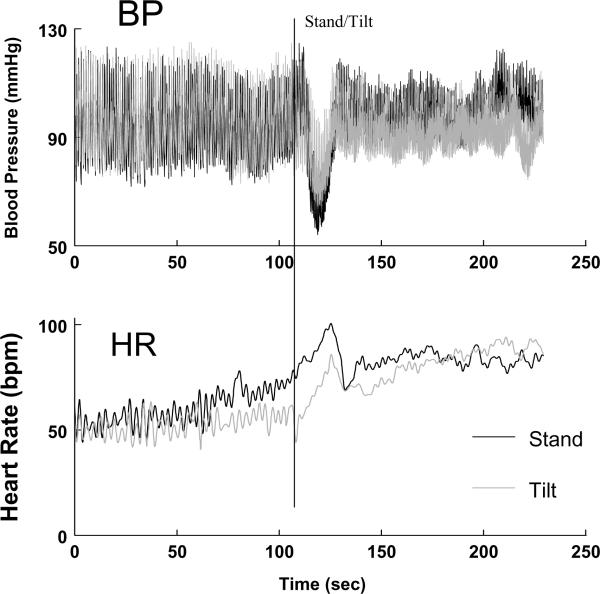
Figure 2.
Rapid standing (black lines) is compared with upright tilt (gray lines) to 70° in the same subject. The upper panel shows changes in blood pressure (BP) and the lower panel shows changes in heart rate (HR). There is a greater fall in BP and rise in HR with standing compared with tilt. Also, both BP and HR increase in anticipation of standing - a phenomenon called “central command”.