Figure 2.
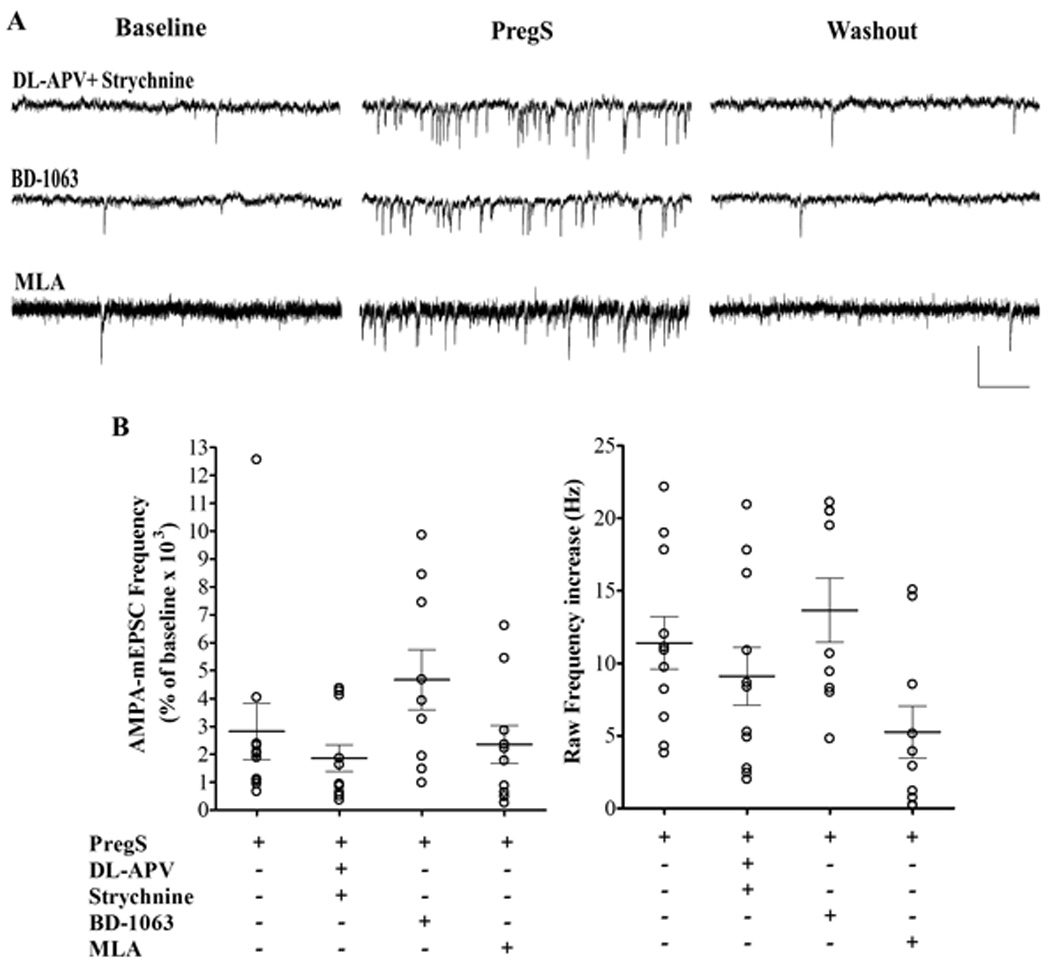
The PregS (25 µM)-induced increase in AMPA-mEPSC frequency is independent of NMDA, glycine, σ1, or α7nACh receptors. (A) Sample traces illustrating the PregS effect on AMPA-mEPSC frequency in PCs from P4-5 rats in the presence of the NMDA and glycine receptors blockers, DL-AP5 (100 µM) and strychnine (1 µM); the σ1 receptor blocker, BD-1063 (1 µM); and the α7nACh receptor blocker, MLA (200nM); calibration: 50 pA and 0.2 s. (B) Summary graphs of the percent frequency (left panel) and the raw frequency increases (right panel) induced by PregS in the presence of NMDA, glycine, σ1 or α7nACh receptor antagonists. For both, percent and raw frequency increases, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test showed no significant difference between controls (n=11) and DL-APV/strychnine (n=11), BD-1063 (n=9) or MLA (n=10). The effect of PregS on AMPA-mEPSC frequency from Fig 1 is shown again for comparison.
