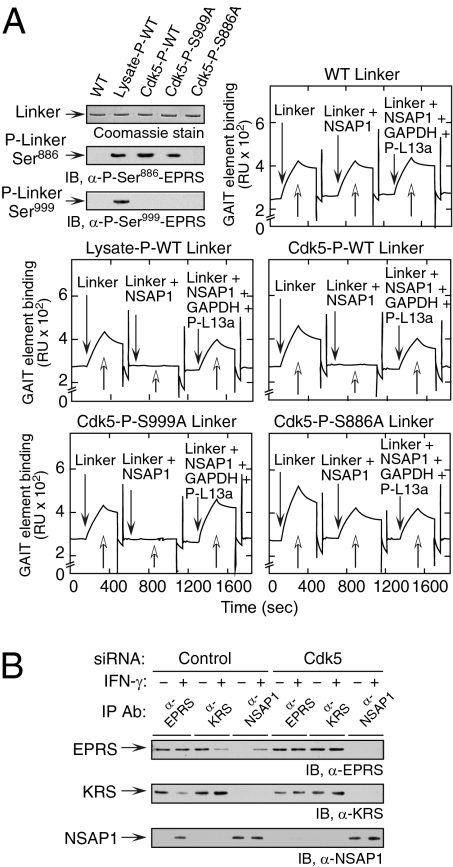
Fig. 4.
Cdk5-mediated EPRS phosphorylation is required for the release of EPRS from the MSC and for binding to GAIT element RNA. (A) EPRS linker phosphorylated at Ser886 by Cdk5 reconstitutes the GAIT complex assembly and binding to GAIT element RNA. His-tagged, WT, and mutant (S886A and S999A) EPRS linker proteins were phosphorylated by incubation with lysate from IFN-γ–treated U937 cells or with recombinant Cdk5/p35, and then repurified using Ni-affinity resin (Top, Left). Specific phosphorylation was confirmed using anti-phosphospecific antibodies. Unmodified (Top, Right), lysate-phosphorylated (Middle, Left), or Cdk5-phosphorylated WT (Middle, Right), S999A (Bottom, Left), and S886A (Bottom, Right) EPRS linkers were preincubated with NSAP1 or with NSAP1, GAPDH, and phospho-L13a (P-L13a), and binding to biotinylated Cp GAIT element RNA immobilized on a streptavidin sensor chip was determined by SPR and expressed as resonance units (RU). (B) Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation induces EPRS release from MSC. U937 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting Cdk5 (and control siRNA) and then treated with IFN-γ for 4 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against EPRS, LysRS (KRS, MSC constituent), and NSAP1 (pre-GAIT complex constituent), and evaluated by immunoblot analysis.