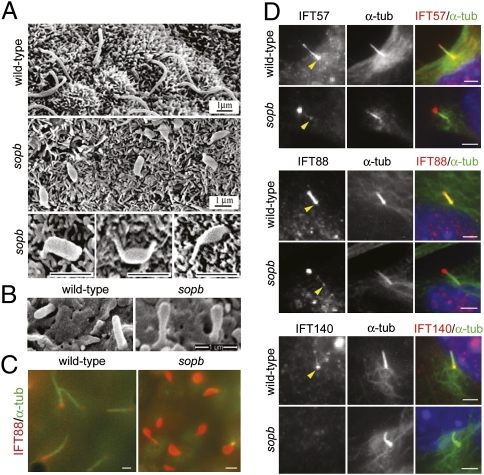
Fig. 3.
Ciliary defects in Ift122sopb mutants. (A) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of cilia in the wild-type and mutant node at head-fold stages. Nodal cilia in the mutant were short, with pronounced swelling along their lengths or at their tips. (B) SEM images of cilia from the e10.5 wild-type and Ift122sopb neuroepithelium at lumbar levels. (C) Mutant nodal cilia showed dramatic accumulation of IFT88 (red). Axonemes were labeled with acetylated α-tubulin (green). (D) Ciliary localization of the complex B IFT proteins IFT57 and IFT88 and the complex A IFT protein IFT140 in wild-type and Ift122sopb pMEFs. IFT57 and IFT88 (red) localize to the base (yellow arrowheads) and along the axoneme (marked by acetylated α-tubulin staining in green) of cilia from wild-type pMEFs, whereas these proteins localized primarily to the tips of the mutant cilia. IFT140 localized to the base and tips of wild-type cilia, but failed to localize to Ift122sopb cilia. Scale bars: 1 μm in A–C and 2 μm in D.