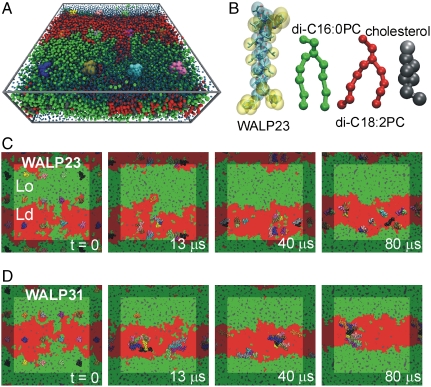
Fig. 1.
Simulation of the sorting and clustering of WALP peptides in a model bilayer with coexisting fluid domains. (A) WALP peptides (colored spheres) embedded in a ternary mixture of di-C16∶0PC (green), di-C18∶2PC (red), and cholesterol (gray), solvated by water (blue). (B) Coarse-grained representation of WALP23 (cyan and yellow), di-C16∶0PC (green), di-C18∶2PC (red), and cholesterol (gray), shown as spheres and sticks. The atomistic structure of the peptide is also shown (sticks). (C and D) Sorting and clustering of WALP23 (C) and WALP31 peptides (D) in the disordered lipid domain.