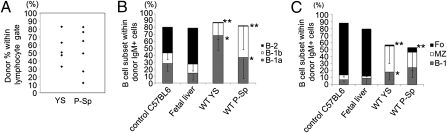
Fig. 2.
Progenitors that reconstitute B-1 and MZ cells are present in YS and P-Sp. The E9.5 WT YS and P-Sp cells were injected into 150 cGy-irradiated NOG neonates immediately after isolation. (A) The level of donor chimerism in the peritoneal cavity of recipient mice (CD45.1+) that received YS- and P-Sp–derived cells (CD45.2+) is depicted. (B) B-cell subsets within donor IgM+ cells in the peritoneal cavity of recipient mice. The percentage of B-1 cells in the peritoneal cavity of YS or P-Sp reconstituted mice was significantly higher than that observed in the peritoneum of nontransplanted adult C57BL/6 mice or E15.5 fetal liver reconstituted mice (P < 0.05). The percentage of B-2 cells in the peritoneal cavity of YS and P-Sp reconstituted animals was significantly less than that observed in the peritoneum of nontransplanted adult control mice or the E15.5 fetal liver reconstituted mice (P < 0.01). The IgMlowIgDhigh or IgMlowCD23high cells were defined as B-2 cells. (C) B-cell subsets within donor IgM+ cells in the spleen. In addition to B-1 cells, the spleen of mice reconstituted with YS and P-Sp cells also contained donor-derived MZ cells. The percentage of FO cells in the spleen of YS and P-Sp transplanted animals was significantly less than nontransplanted control C57BL/6 mice or fetal liver reconstituted mice (P < 0.01). The percentage of MZ cells in the spleen of YS and P-Sp transplanted mice was significantly higher than nontransplanted control mice or E15.5 fetal liver reconstituted mice (P < 0.05). The number of animals examined in each group is listed in Table S1.