Fig. 5.
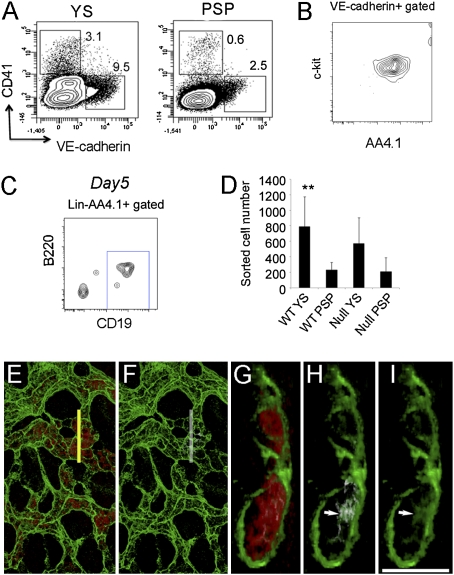
B-1 B progenitor cells are derived from VE-cadherin+CD41− hemogenic endothelial cells. (A) VE-cadherin+CD41− (endothelial) cells or VE-cadherin−CD41+ (hematopoietic) cells were sorted from E9.5 WT and Ncx1−/− YS and P-Sp cells and plated on OP9 with IL7 and flt-3 ligand. WT FACS dot plots are depicted. Ncx1−/− embryos displayed a similar phenotype. (B) All VE-cadherin+CD41− cells coexpressed AA4.1 and c-kit (n = 3). (C) After 5 d of culture, VE-cadherin+CD41− cells from Ncx1−/− YS produced AA4.1+CD19+B220dim cells in vitro (representative of four experiments). (D) The number of VE-cadherin+ cells obtained from one embryo equivalent (1 e.e.) is depicted. WT YS VE-cad+ cell number was significantly higher than WT P-Sp cell number (P < 0.01). (E–I) Emergence of CD19+ (white, white arrow) cells was detected as a small regionalized population of hematopoietic cells (red) within the E9.0 YS VE-cadherin+ vasculature (green). (E) Image of the E9.0 yolk sac showing hematopoietic cells (red) within the VE-cadherin+ (green) vasculature. (F) Same region as in E depicting small CD19dim (white) population. (G) Orthogonal α-projections (4× zoom) of the region indicated by the yellow line in E. (h and I) Arrows indicate rare CD19+ (white) VE-cadherin (green) double-positive cells. (I) VE-cad+ cells (green) are highlighted. (Scale bar: 100 μm in E and F and 25 μm in G–I.)