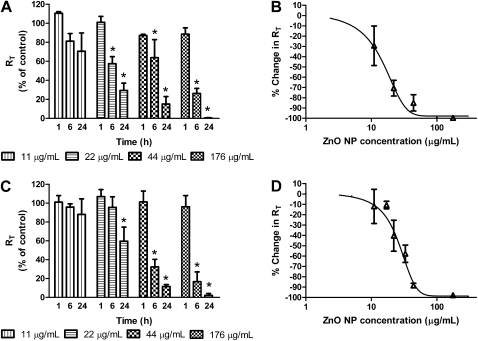
Figure 1.
Effects of apical exposure to spherical zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) on RT of minimal defined serum-free medium (MDSF) (A)- or MDSF supplemented with 10% newborn bovine serum (MDS) (C)-grown rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers (RAECMs) after 1, 6, and 24 hours. RAECMs were exposed apically to ZnO NPs at 11, 22, 44, and 176 μg/ml. RT of MDSF- and MDS-grown RAECMs before ZnO NP exposure was 2.33 (±0.37) kΩcm2 (n = 27) and 2.63 (±0.47) kΩcm2 (n = 33), respectively. Dose–response curves after 24-hour exposure are shown for RT of MDSF (B)- or MDS (D)-grown RAECMs versus ZnO NPs. *Significantly different (P < 0.05) from control (RAECMs not exposed to ZnO NPs).