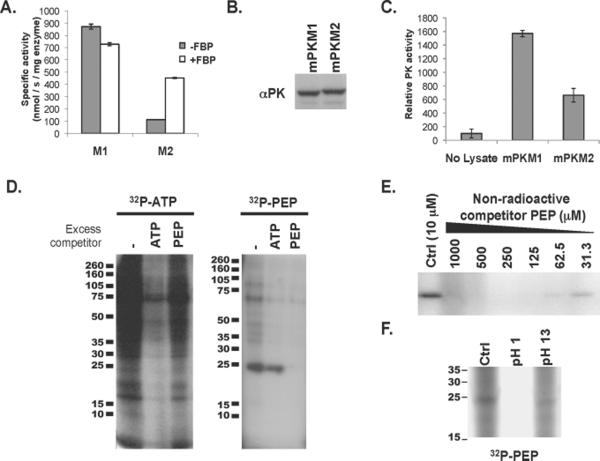
Fig. 1. Evidence of PEP-dependent phosphorylation of a 25-kD protein in PKM2 expressing cells with less pyruvate kinase activity.
A. 6xHis-tagged human PKM1 and PKM2 were expressed in E. coli and purified by Ni-affinity chromatography. The specific activity of each enzyme was determined in the presence of saturating amounts of PEP and ADP. The activity of PKM1 and PKM2 in the presence and absence of FBP is shown.
B. H1299 cells were engineered to express equivalent amount of PKM1 or PKM2 protein as described previously (4). Equivalent expression of PKM1 and PKM2 was confirmed by Western blot using an antibody (αPK) that recognizes an epitope shared by PKM1 and PKM2 as shown.
C. As in (A), pyruvate kinase activity was determined using saturating amounts of PEP and ADP. The relative pyruvate kinase activity observed in the PKM1- or PKM2-expressing cells described in (B), relative to lysis buffer alone, is shown.
D. HEK293 cells were hypotonically lysed and incubated with 32P-labeled ATP or 32P-labeled PEP prior to analysis by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The lysates were incubated with 32P-labeled ATP or 32P-labeled PEP in the presence of 10 μM ATP or PEP respectively (−), or with the addition of 1 mM non-radioactive competitor ATP or PEP as shown.
E. Cell lysate was incubated with 32P-labeled PEP in the presence of the indicated concentration of non-radioactive competitor PEP prior to analysis by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography as shown.
F. Cell lysate was incubated with 32P-labeled PEP as above and the pH of the reaction was changed to pH 1 or pH 13 as indicated. Reactions were incubated for 2 hours at 65° C prior to analysis by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography as shown.