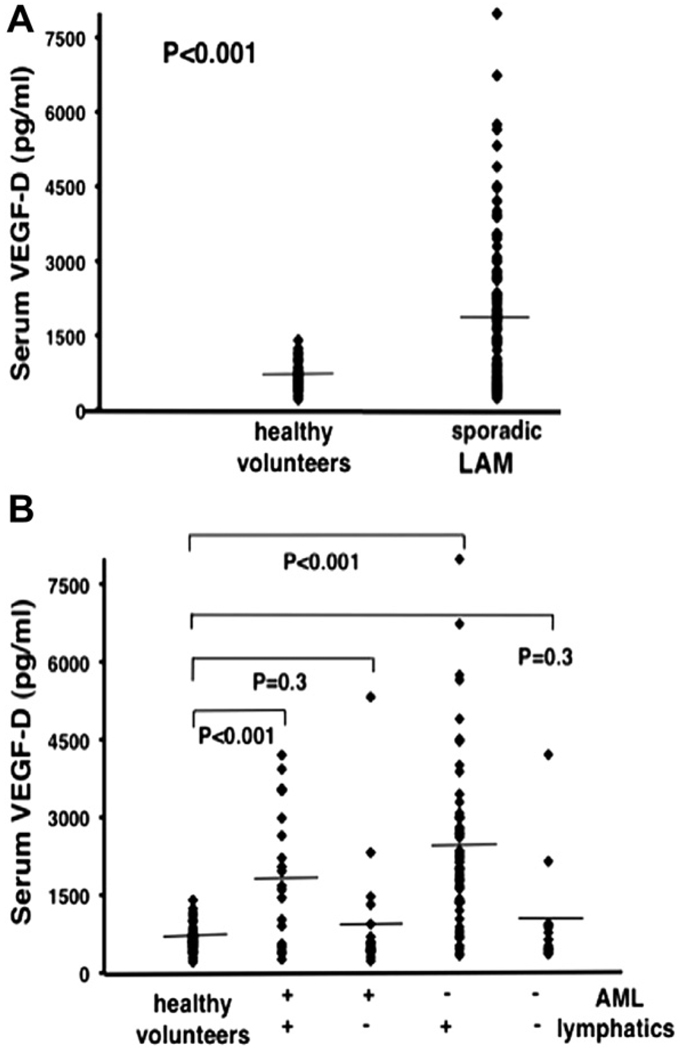
Figure 4.
Serum Levels of VEGF-D in Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. In Panel A, serum VEGF-D levels in all patients with sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (n = 111) were compared to those of healthy volunteers (n = 40). Panel B shows patient samples compared on the basis of thoracic or abdominal lymphatic involvement (presence (n = 77) or absence (n = 34) of lymphangioleiomyomas and/or adenopathy) and the presence (n = 40) or absence (n = 71) of renal angiomyolipomas (AMLs). All groups were compared to healthy volunteers (n = 40). (+) = presence of, (−) = absence of. Each ♦ represents serum measurement of VEGF-D from one patient or healthy volunteer. Lines represent mean values (From reference 74).